Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and they play a crucial role in determining the properties of the substances around us. One of the most important concepts in chemistry is the formation of bonds between atoms, which is essential for the creation of molecules and the structure of matter as we know it. In this article, we will explore the reasons why atoms form bonds and delve into the world of atomic interactions.

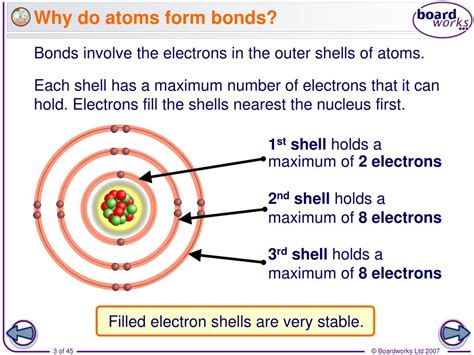
Atoms are driven to form bonds due to their desire to achieve a stable electronic configuration. This stability is often achieved when an atom has a full outer energy level, similar to the noble gases. When atoms share or exchange electrons to achieve this stable configuration, they form bonds. This is the foundation of the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level with eight electrons.
Reason 1: Atoms Seek Stability
Atoms form bonds to achieve stability and reduce their energy state. When atoms are in their ground state, they have a specific number of electrons in their outermost energy level. However, when they react with other atoms, they can gain or lose electrons to achieve a more stable configuration. This stability is often achieved when an atom has a full outer energy level, similar to the noble gases. For example, when sodium (Na) reacts with chlorine (Cl), they form sodium chloride (NaCl), where sodium loses an electron to achieve a stable configuration, and chlorine gains an electron to achieve a stable configuration.

Reason 2: Electrons Occupy Space
Electrons occupy space around the nucleus of an atom, and when atoms form bonds, they share this space. This sharing of space allows atoms to achieve a more stable configuration and reduces their energy state. The concept of electron density is essential in understanding how atoms form bonds. Electron density refers to the probability of finding an electron in a particular region around the nucleus. When atoms share electrons, they create a region of high electron density between them, which holds them together.

Reason 3: Atoms Form Bonds to Reduce Energy
Atoms form bonds to reduce their energy state. When atoms are in their ground state, they have a specific amount of energy. However, when they react with other atoms, they can release or absorb energy to achieve a more stable configuration. This energy change is often referred to as the bond energy. For example, when hydrogen (H) reacts with oxygen (O), they form water (H2O), which releases energy and forms a more stable configuration.

Reason 4: Atoms Form Bonds to Increase Entropy
Atoms form bonds to increase entropy, which is a measure of disorder or randomness. When atoms are in their ground state, they have a specific amount of entropy. However, when they react with other atoms, they can increase their entropy by forming bonds. This increase in entropy is often referred to as the entropy change. For example, when carbon (C) reacts with oxygen (O), they form carbon dioxide (CO2), which increases entropy and forms a more stable configuration.

Reason 5: Atoms Form Bonds to Create Molecules
Atoms form bonds to create molecules, which are the building blocks of matter. When atoms share or exchange electrons, they form bonds, which hold them together and create a molecule. This molecule can have unique properties, such as shape, size, and reactivity, which are determined by the bonds between the atoms. For example, when hydrogen (H) reacts with oxygen (O), they form water (H2O), which is a molecule with unique properties, such as its ability to dissolve substances.

In conclusion, atoms form bonds for several reasons, including seeking stability, occupying space, reducing energy, increasing entropy, and creating molecules. These reasons are fundamental to understanding the world of chemistry and the structure of matter as we know it. By understanding why atoms form bonds, we can gain insight into the properties of substances and the reactions that occur between them.
What is the main reason why atoms form bonds?
+Atoms form bonds to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
What is the octet rule?
+The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level with eight electrons.
What is electron density?
+Electron density refers to the probability of finding an electron in a particular region around the nucleus.