As a taxpayer, navigating the world of tax forms can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding the nuances of Schedule 2. The Schedule 2 tax form is a crucial component of the tax return process, and it's essential to grasp its significance to avoid any potential errors or penalties. In this article, we will break down the complexities of Schedule 2 into 5 easy-to-follow steps, making it simpler for you to comprehend and accurately complete this critical tax form.
The Importance of Schedule 2
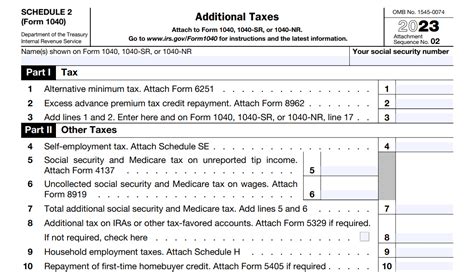
Before diving into the nitty-gritty of Schedule 2, it's essential to understand its purpose. Schedule 2 is a supplemental tax form that reports additional taxes, such as self-employment tax, unreported Social Security and Medicare tax, and tax on tips. This form is used to calculate the total tax liability, which is then reported on the main tax return form, typically Form 1040. The accuracy of Schedule 2 is crucial, as it directly affects the overall tax bill.
Step 1: Determine if You Need to File Schedule 2
Not everyone needs to file Schedule 2. This form is typically required for individuals who have income that is not subject to withholding, such as self-employment income, tips, or unreported Social Security and Medicare tax. If you're unsure whether you need to file Schedule 2, consider the following scenarios:
- You're self-employed and have a net earnings from self-employment of $400 or more.
- You received tips that were not reported to your employer.
- You have unreported Social Security and Medicare tax.
- You have other additional taxes, such as tax on unemployment compensation.
If any of these scenarios apply to you, it's likely you'll need to file Schedule 2.

Step 2: Gather Required Information
To accurately complete Schedule 2, you'll need to gather specific information, including:
- Your self-employment income and expenses (if applicable).
- The amount of tips you received (if applicable).
- Your Social Security and Medicare tax information (if applicable).
- Your unemployment compensation information (if applicable).
It's essential to have all the necessary documents, such as your tax return from the previous year, your W-2 forms, and any relevant receipts or invoices.
Step 3: Complete the Form
Once you have all the required information, it's time to complete Schedule 2. The form is divided into several sections, each addressing a specific type of additional tax. Be sure to follow these steps:
- Section 1: Self-employment tax. Report your net earnings from self-employment and calculate your self-employment tax.
- Section 2: Unreported Social Security and Medicare tax. Report any unreported Social Security and Medicare tax.
- Section 3: Tax on tips. Report any tips you received that were not reported to your employer.
- Section 4: Other additional taxes. Report any other additional taxes, such as tax on unemployment compensation.
Be sure to accurately complete each section, as errors can lead to delays or penalties.

Step 4: Calculate Your Total Tax Liability
Once you've completed Schedule 2, you'll need to calculate your total tax liability. This involves adding the additional taxes reported on Schedule 2 to your total tax liability on Form 1040. Be sure to follow these steps:
- Calculate your total tax liability on Form 1040.
- Add the additional taxes reported on Schedule 2 to your total tax liability on Form 1040.
- Report the total tax liability on Form 1040.
Step 5: Review and Submit
The final step is to review your completed Schedule 2 and Form 1040 for accuracy. Double-check your calculations, and ensure you've reported all required information. Once you're satisfied with the accuracy of your forms, submit them to the IRS.
Tips for Completing Schedule 2
To ensure a smooth and accurate completion of Schedule 2, keep the following tips in mind:
- Use the correct form. Make sure you're using the most recent version of Schedule 2.
- Report all required information. Ensure you've reported all necessary information, including self-employment income, tips, and unreported Social Security and Medicare tax.
- Calculate accurately. Double-check your calculations to avoid errors.
- Seek professional help. If you're unsure about completing Schedule 2, consider consulting a tax professional.

Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about Schedule 2:
What is Schedule 2 used for?
+Schedule 2 is used to report additional taxes, such as self-employment tax, unreported Social Security and Medicare tax, and tax on tips.
Do I need to file Schedule 2 if I'm not self-employed?
+Maybe. If you have other additional taxes, such as unreported Social Security and Medicare tax or tax on tips, you may still need to file Schedule 2.
Can I file Schedule 2 electronically?
+Yes. You can file Schedule 2 electronically using tax software or by visiting the IRS website.
By following these 5 easy steps and tips, you'll be well on your way to accurately completing Schedule 2 and avoiding any potential errors or penalties. Remember to review your forms carefully and seek professional help if needed. Don't hesitate to reach out to a tax professional or the IRS if you have any questions or concerns.