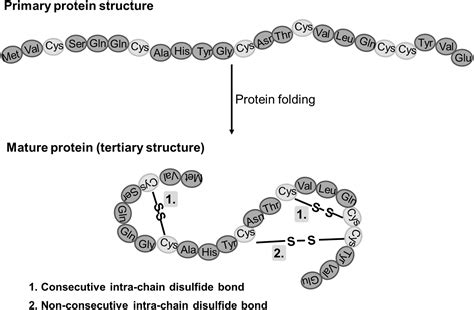
Disulfide bonds are a crucial aspect of protein structure and function, playing a key role in maintaining the stability and integrity of proteins. These bonds are formed between two cysteine residues, which contain a thiol group (-SH) that can participate in a disulfide exchange reaction. This reaction leads to the formation of a sulfur-sulfur bond, also known as a disulfide bond.
The importance of disulfide bonds in proteins cannot be overstated. They are essential for the proper folding of proteins, helping to maintain their three-dimensional structure and ensuring that they function correctly. Disulfide bonds also play a role in the stability of proteins, protecting them from denaturation and degradation. In this article, we will explore five places where disulfide bonds form in proteins, highlighting their significance and providing examples of their role in protein function.
Extracellular Proteins

Extracellular proteins, such as those found in the blood or extracellular matrix, are often stabilized by disulfide bonds. These proteins are exposed to harsh environments and must be able to withstand proteolytic degradation, oxidative stress, and other forms of damage. Disulfide bonds help to maintain the structure of these proteins, ensuring that they remain functional and stable.
For example, the protein lysozyme, which is found in tears and saliva, contains four disulfide bonds that help to maintain its structure and function. Lysozyme is an enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls, and its disulfide bonds play a crucial role in its ability to withstand the harsh conditions of the extracellular environment.
Importance of Disulfide Bonds in Extracellular Proteins
Disulfide bonds are essential for the stability and function of extracellular proteins. They help to:
- Maintain protein structure and function
- Protect proteins from proteolytic degradation
- Ensure proper protein folding and assembly
- Regulate protein activity and function
Membrane Proteins

Membrane proteins, which span the cell membrane, also rely on disulfide bonds for stability and function. These proteins are often exposed to harsh environments, including high temperatures, oxidative stress, and proteolytic degradation. Disulfide bonds help to maintain the structure of membrane proteins, ensuring that they remain functional and stable.
For example, the protein rhodopsin, which is found in the retina, contains a disulfide bond that helps to maintain its structure and function. Rhodopsin is a light-sensitive protein that plays a crucial role in vision, and its disulfide bond is essential for its proper function.
Importance of Disulfide Bonds in Membrane Proteins
Disulfide bonds are essential for the stability and function of membrane proteins. They help to:
- Maintain protein structure and function
- Regulate protein activity and function
- Ensure proper protein folding and assembly
- Protect proteins from proteolytic degradation
Cytosolic Proteins

Cytosolic proteins, which are found in the cytosol of cells, can also contain disulfide bonds. While the cytosol is generally a reducing environment, some cytosolic proteins require disulfide bonds for stability and function.
For example, the protein thioredoxin, which is found in the cytosol, contains a disulfide bond that helps to regulate its activity. Thioredoxin is a protein that plays a crucial role in redox regulation, and its disulfide bond is essential for its proper function.
Importance of Disulfide Bonds in Cytosolic Proteins
Disulfide bonds are essential for the stability and function of some cytosolic proteins. They help to:
- Regulate protein activity and function
- Ensure proper protein folding and assembly
- Protect proteins from proteolytic degradation
- Maintain protein structure and function
Nuclear Proteins

Nuclear proteins, which are found in the nucleus of cells, can also contain disulfide bonds. While the nucleus is generally a reducing environment, some nuclear proteins require disulfide bonds for stability and function.
For example, the protein Ku, which is found in the nucleus, contains a disulfide bond that helps to regulate its activity. Ku is a protein that plays a crucial role in DNA repair, and its disulfide bond is essential for its proper function.
Importance of Disulfide Bonds in Nuclear Proteins
Disulfide bonds are essential for the stability and function of some nuclear proteins. They help to:
- Regulate protein activity and function
- Ensure proper protein folding and assembly
- Protect proteins from proteolytic degradation
- Maintain protein structure and function
Viral Proteins

Viral proteins, which are found in viruses, can also contain disulfide bonds. These proteins are often exposed to harsh environments, including high temperatures, oxidative stress, and proteolytic degradation. Disulfide bonds help to maintain the structure of viral proteins, ensuring that they remain functional and stable.
For example, the protein hemagglutinin, which is found in the influenza virus, contains disulfide bonds that help to maintain its structure and function. Hemagglutinin is a protein that plays a crucial role in viral entry, and its disulfide bonds are essential for its proper function.
Importance of Disulfide Bonds in Viral Proteins
Disulfide bonds are essential for the stability and function of viral proteins. They help to:
- Maintain protein structure and function
- Regulate protein activity and function
- Ensure proper protein folding and assembly
- Protect proteins from proteolytic degradation
In conclusion, disulfide bonds play a crucial role in the stability and function of proteins. They are found in a variety of proteins, including extracellular proteins, membrane proteins, cytosolic proteins, nuclear proteins, and viral proteins. Understanding the importance of disulfide bonds in these proteins can provide valuable insights into their structure and function, and can help to inform the development of new therapeutic strategies.
If you have any questions or comments about disulfide bonds in proteins, please leave them below. We would love to hear from you!
What is a disulfide bond?
+A disulfide bond is a type of covalent bond that forms between two cysteine residues in a protein. It is a sulfur-sulfur bond that helps to maintain the structure and stability of the protein.
Where are disulfide bonds found in proteins?
+Disulfide bonds are found in a variety of proteins, including extracellular proteins, membrane proteins, cytosolic proteins, nuclear proteins, and viral proteins.
What is the importance of disulfide bonds in proteins?
+Disulfide bonds are essential for the stability and function of proteins. They help to maintain protein structure and function, regulate protein activity and function, ensure proper protein folding and assembly, and protect proteins from proteolytic degradation.