Lipid bilayers are a crucial component of cell membranes, providing a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the movement of molecules in and out of cells. But have you ever wondered how these complex structures form in the first place? The answer lies in the unique properties of lipids and the principles of thermodynamics.

What are Lipid Bilayers?
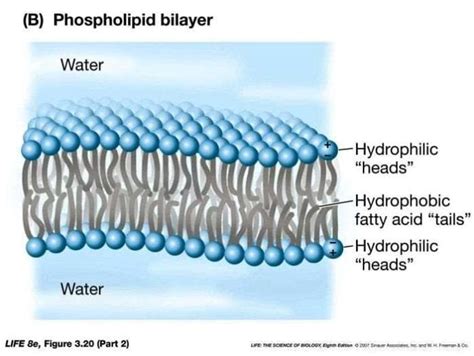
A lipid bilayer is a double layer of lipids, with the hydrophilic (water-loving) heads facing outwards and the hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails facing inwards. This arrangement creates a stable and flexible structure that is essential for maintaining cell membrane integrity. Lipid bilayers are composed of various types of lipids, including phospholipids, cholesterol, and glycolipids, which provide a unique set of properties that enable cells to function properly.
Self-Assembly of Lipid Bilayers
One of the most fascinating aspects of lipid bilayers is their ability to form spontaneously through a process known as self-assembly. This phenomenon occurs when lipids are dispersed in water and are free to interact with each other. The hydrophobic tails of the lipids aggregate together, forming a hydrophobic core, while the hydrophilic heads face outwards, interacting with the surrounding water.
The self-assembly of lipid bilayers is driven by the principles of thermodynamics, which dictate that systems will tend towards a state of minimum energy. In this case, the lipids minimize their energy by aggregating together and forming a bilayer structure. This process is facilitated by the unique properties of lipids, including their amphiphilic nature and their ability to form hydrogen bonds with water.
The Role of Thermodynamics in Lipid Bilayer Formation
Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in the formation of lipid bilayers. The process of self-assembly is driven by the tendency of lipids to minimize their energy, which is influenced by the following factors:
-
Hydrophobic Effect
The hydrophobic effect is a major driving force behind the self-assembly of lipid bilayers. This phenomenon occurs when non-polar molecules, such as the hydrophobic tails of lipids, are dispersed in water. The non-polar molecules aggregate together, minimizing their contact with water and reducing their energy.
-
Entropy
Entropy is another important factor in lipid bilayer formation. The process of self-assembly is accompanied by an increase in entropy, as the lipids become more disordered and random in their arrangement. This increase in entropy is favorable, as it allows the system to tend towards a state of maximum disorder.
-
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is the energy associated with the formation of hydrogen bonds between lipids and water. The formation of these bonds is favorable, as it allows the lipids to interact with the surrounding water and stabilize the bilayer structure.

Factors Influencing Lipid Bilayer Formation
Several factors can influence the formation of lipid bilayers, including:
-
Temperature
Temperature can affect the rate of lipid bilayer formation, with higher temperatures favoring the process.
-
pH
pH can influence the ionization state of lipids, which can affect their ability to form bilayers.
-
Concentration
The concentration of lipids can influence the rate of bilayer formation, with higher concentrations favoring the process.
-
Presence of Other Molecules
The presence of other molecules, such as proteins or cholesterol, can influence the formation of lipid bilayers.
Biological Significance of Lipid Bilayers
Lipid bilayers play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
-
Cell Signaling
Lipid bilayers can facilitate cell signaling by allowing the movement of signaling molecules across the cell membrane.
-
Transport of Molecules
Lipid bilayers can regulate the transport of molecules across the cell membrane, allowing cells to control their internal environment.
-
Cell Adhesion
Lipid bilayers can facilitate cell adhesion by allowing cells to interact with each other and with the surrounding environment.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the spontaneous formation of lipid bilayers is a fascinating phenomenon that is driven by the principles of thermodynamics. Understanding the science behind this process is crucial for appreciating the complex structure and function of cell membranes. By recognizing the importance of lipid bilayers, we can gain insights into various biological processes and develop new approaches for treating diseases.
What is the main driving force behind the self-assembly of lipid bilayers?
+The main driving force behind the self-assembly of lipid bilayers is the hydrophobic effect, which occurs when non-polar molecules, such as the hydrophobic tails of lipids, are dispersed in water.
What is the role of thermodynamics in lipid bilayer formation?
+Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in the formation of lipid bilayers, with the process of self-assembly being driven by the tendency of lipids to minimize their energy.
What are some factors that can influence the formation of lipid bilayers?
+Several factors can influence the formation of lipid bilayers, including temperature, pH, concentration, and the presence of other molecules.