Understanding Covalent Bonds: A Deep Dive

In the world of chemistry, atoms are the building blocks of matter, and they interact with each other in various ways to form different types of bonds. One of the most common types of bonds is the covalent bond, which is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Covalent bonds are typically formed between two nonmetal atoms, which are atoms that are not metals.
In this article, we will explore the world of covalent bonds, including the types of atoms that typically form them, the characteristics of covalent bonds, and the various types of covalent bonds that exist. We will also discuss the importance of covalent bonds in chemistry and provide examples of molecules that are held together by covalent bonds.
Atoms That Typically Form Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are typically formed between two nonmetal atoms, which are atoms that are not metals. These atoms are usually found in the upper right corner of the periodic table and include elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine. Nonmetal atoms tend to have a high electronegativity, which means that they have a strong tendency to attract electrons towards themselves.
When two nonmetal atoms interact with each other, they share one or more pairs of electrons to form a covalent bond. This sharing of electrons allows the atoms to achieve a full outer energy level, which is a stable configuration. Covalent bonds are typically strong and stable, and they are responsible for holding together many different types of molecules.
Characteristics of Covalent Bonds

Covalent bonds have several characteristics that distinguish them from other types of bonds. Some of the key characteristics of covalent bonds include:
- Sharing of electrons: Covalent bonds involve the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between atoms.
- Nonmetal atoms: Covalent bonds are typically formed between two nonmetal atoms.
- High electronegativity: Nonmetal atoms tend to have a high electronegativity, which means that they have a strong tendency to attract electrons towards themselves.
- Strong and stable: Covalent bonds are typically strong and stable, and they are responsible for holding together many different types of molecules.
- Variable bond length: The length of a covalent bond can vary depending on the atoms involved and the type of bond.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are several types of covalent bonds, including:
- Sigma bonds: Sigma bonds are formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons in a head-on manner.
- Pi bonds: Pi bonds are formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons in a side-by-side manner.
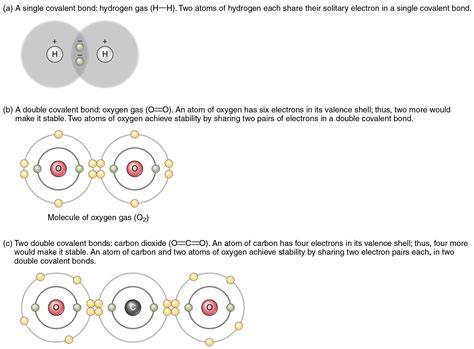
- Single bonds: Single bonds are formed when two atoms share one pair of electrons.
- Double bonds: Double bonds are formed when two atoms share two pairs of electrons.
- Triple bonds: Triple bonds are formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons.
Importance of Covalent Bonds

Covalent bonds play a crucial role in chemistry and are responsible for holding together many different types of molecules. Some of the importance of covalent bonds include:
- Molecular structure: Covalent bonds determine the structure of molecules and are responsible for the shape and properties of molecules.
- Chemical reactions: Covalent bonds are involved in many chemical reactions and are responsible for the formation of new molecules.
- Biological molecules: Covalent bonds are found in many biological molecules, including DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Materials science: Covalent bonds are responsible for the properties of many materials, including plastics, ceramics, and glass.
Examples of Molecules Held Together by Covalent Bonds
Some examples of molecules that are held together by covalent bonds include:
- Water: Water molecules are held together by covalent bonds between oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
- Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide molecules are held together by covalent bonds between carbon and oxygen atoms.
- Methane: Methane molecules are held together by covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- DNA: DNA molecules are held together by covalent bonds between sugar and phosphate molecules.
In conclusion, covalent bonds are a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. They are typically formed between two nonmetal atoms and are responsible for holding together many different types of molecules. Understanding covalent bonds is important for understanding many different aspects of chemistry and is crucial for understanding the structure and properties of molecules.
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about covalent bonds, please leave a comment below.