Ionic bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding which elements form ionic bonds is crucial for grasping various chemical reactions and compound formations. Ionic bonds occur when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. These ions are then attracted to each other, forming a strong chemical bond.
The unique properties of elements, such as their electronegativity and electron configuration, determine whether they can form ionic bonds. Typically, ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals. In this article, we will explore six element pairs that commonly form ionic bonds.
Understanding Ionic Bonds

Before we dive into the specific element pairs, it's essential to understand the basics of ionic bonds. Ionic bonds are typically formed between a metal and a nonmetal. The metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, known as a cation. The nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion, known as an anion. The electrostatic attraction between the cation and anion forms the ionic bond.
Element Pair 1: Sodium (Na) and Chlorine (Cl)

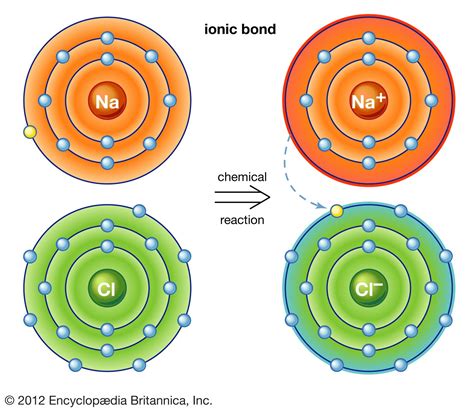
Sodium and chlorine are a classic example of elements that form ionic bonds. Sodium is a highly reactive metal that readily loses an electron to form a positively charged ion (Na+). Chlorine, on the other hand, is a highly reactive nonmetal that readily gains an electron to form a negatively charged ion (Cl-). When sodium and chlorine react, they form sodium chloride (NaCl), also known as table salt.
How It Works
The reaction between sodium and chlorine can be represented by the following equation:
Na (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2NaCl (s)
In this reaction, sodium loses an electron to form a positively charged ion, while chlorine gains an electron to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the sodium cation and the chloride anion forms the ionic bond.
Element Pair 2: Calcium (Ca) and Oxygen (O)

Calcium and oxygen are another element pair that forms ionic bonds. Calcium is a metal that readily loses two electrons to form a positively charged ion (Ca2+). Oxygen is a nonmetal that readily gains two electrons to form a negatively charged ion (O2-). When calcium and oxygen react, they form calcium oxide (CaO), also known as quicklime.
How It Works
The reaction between calcium and oxygen can be represented by the following equation:
Ca (s) + O2 (g) → 2CaO (s)
In this reaction, calcium loses two electrons to form a positively charged ion, while oxygen gains two electrons to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the calcium cation and the oxide anion forms the ionic bond.
Element Pair 3: Magnesium (Mg) and Nitrogen (N)

Magnesium and nitrogen are another element pair that forms ionic bonds. Magnesium is a metal that readily loses two electrons to form a positively charged ion (Mg2+). Nitrogen is a nonmetal that readily gains three electrons to form a negatively charged ion (N3-). When magnesium and nitrogen react, they form magnesium nitride (Mg3N2).
How It Works
The reaction between magnesium and nitrogen can be represented by the following equation:
3Mg (s) + N2 (g) → Mg3N2 (s)
In this reaction, magnesium loses two electrons to form a positively charged ion, while nitrogen gains three electrons to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the magnesium cation and the nitride anion forms the ionic bond.
Element Pair 4: Aluminum (Al) and Sulfur (S)

Aluminum and sulfur are another element pair that forms ionic bonds. Aluminum is a metal that readily loses three electrons to form a positively charged ion (Al3+). Sulfur is a nonmetal that readily gains two electrons to form a negatively charged ion (S2-). When aluminum and sulfur react, they form aluminum sulfide (Al2S3).
How It Works
The reaction between aluminum and sulfur can be represented by the following equation:
2Al (s) + 3S (s) → Al2S3 (s)
In this reaction, aluminum loses three electrons to form a positively charged ion, while sulfur gains two electrons to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the aluminum cation and the sulfide anion forms the ionic bond.
Element Pair 5: Lithium (Li) and Fluorine (F)

Lithium and fluorine are another element pair that forms ionic bonds. Lithium is a metal that readily loses an electron to form a positively charged ion (Li+). Fluorine is a nonmetal that readily gains an electron to form a negatively charged ion (F-). When lithium and fluorine react, they form lithium fluoride (LiF).
How It Works
The reaction between lithium and fluorine can be represented by the following equation:
Li (s) + F2 (g) → 2LiF (s)
In this reaction, lithium loses an electron to form a positively charged ion, while fluorine gains an electron to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the lithium cation and the fluoride anion forms the ionic bond.
Element Pair 6: Potassium (K) and Iodine (I)

Potassium and iodine are another element pair that forms ionic bonds. Potassium is a metal that readily loses an electron to form a positively charged ion (K+). Iodine is a nonmetal that readily gains an electron to form a negatively charged ion (I-). When potassium and iodine react, they form potassium iodide (KI).
How It Works
The reaction between potassium and iodine can be represented by the following equation:
K (s) + I2 (g) → 2KI (s)
In this reaction, potassium loses an electron to form a positively charged ion, while iodine gains an electron to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the potassium cation and the iodide anion forms the ionic bond.
In conclusion, ionic bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding which elements form ionic bonds is crucial for grasping various chemical reactions and compound formations. The six element pairs discussed in this article are common examples of elements that form ionic bonds. By understanding the unique properties of these elements and how they react with each other, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of chemistry.
What is an ionic bond?
+An ionic bond is a chemical bond that forms between two ions with opposite charges. Typically, ionic bonds form between a metal and a nonmetal.
What are the characteristics of elements that form ionic bonds?
+Elements that form ionic bonds typically have a large difference in electronegativity, with metals having a low electronegativity and nonmetals having a high electronegativity. Additionally, metals tend to lose electrons to form positively charged ions, while nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form negatively charged ions.
What are some common element pairs that form ionic bonds?
+Some common element pairs that form ionic bonds include sodium and chlorine, calcium and oxygen, magnesium and nitrogen, aluminum and sulfur, lithium and fluorine, and potassium and iodine.