Understanding Hydrogen Bonds and Their Role in Water Molecules

Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and properties of water molecules. These weak electrostatic attractions between molecules are responsible for many of the unique characteristics of water, including its high surface tension, boiling point, and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances. In this article, we will explore the concept of hydrogen bonds, how they form, and their significance in water molecules.
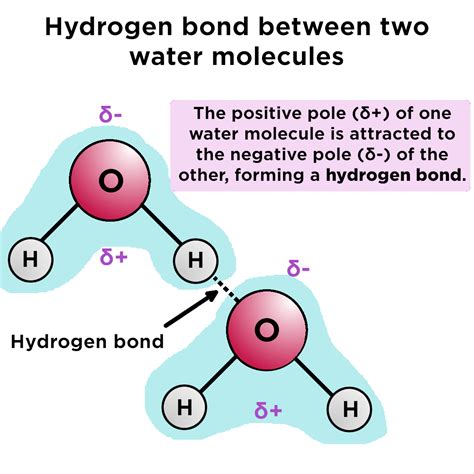
The properties of water are essential for life on Earth, and understanding the hydrogen bonds that hold water molecules together is crucial for appreciating the complexities of biological systems. Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that arises from the interaction between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, and another electronegative atom. In the case of water molecules, hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atoms bonded to oxygen and other oxygen atoms.
The Formation of Hydrogen Bonds in Water Molecules
The formation of hydrogen bonds in water molecules occurs through a combination of electrostatic and covalent interactions. Water molecules are polar, meaning they have a slight positive charge on the hydrogen atoms and a slight negative charge on the oxygen atom. This polarity allows the hydrogen atoms to form weak bonds with the oxygen atoms of neighboring molecules.
The process of hydrogen bond formation involves the following steps:
- The oxygen atom in a water molecule shares its electrons with the hydrogen atoms, creating a covalent bond.
- The electronegative oxygen atom pulls the shared electrons closer to itself, creating a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms.
- The partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms is attracted to the partial negative charge on the oxygen atoms of neighboring molecules.
- The weak electrostatic attraction between the hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms forms a hydrogen bond.
The Significance of Hydrogen Bonds in Water Molecules

Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and properties of water molecules, including:
- High surface tension: Hydrogen bonds between water molecules at the surface create a "skin" that allows water to resist external forces, such as gravity, and maintain its shape against gravity.
- High boiling point: Hydrogen bonds require a significant amount of energy to break, which is why water has a relatively high boiling point compared to other substances.
- Solubility: Hydrogen bonds allow water to dissolve a wide range of substances by forming bonds with the solute molecules.
- Viscosity: Hydrogen bonds contribute to the viscosity of water by creating a network of interactions between molecules that resists flow.
The Role of Hydrogen Bonds in Biological Systems
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in many biological systems, including:
- Protein structure: Hydrogen bonds help to stabilize the three-dimensional structure of proteins by forming bonds between amino acids.
- DNA structure: Hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of DNA together, allowing the molecule to maintain its double helix structure.
- Cell membrane structure: Hydrogen bonds help to maintain the structure of cell membranes by forming bonds between phospholipid molecules.
Conclusion: The Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Water Molecules

In conclusion, hydrogen bonds are a crucial aspect of water molecules, playing a significant role in their structure and properties. Understanding the formation and significance of hydrogen bonds is essential for appreciating the complexities of biological systems. The unique characteristics of water, including its high surface tension, boiling point, and solubility, are all dependent on the hydrogen bonds that hold water molecules together.
We encourage you to share your thoughts on the importance of hydrogen bonds in water molecules. How do you think the properties of water contribute to its essential role in biological systems? Share your comments below!
What is the definition of a hydrogen bond?
+A hydrogen bond is a type of intermolecular force that arises from the interaction between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Why are hydrogen bonds important in water molecules?
+Hydrogen bonds are important in water molecules because they contribute to the high surface tension, boiling point, and solubility of water, making it an essential component of biological systems.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in protein structure?
+Hydrogen bonds help to stabilize the three-dimensional structure of proteins by forming bonds between amino acids.