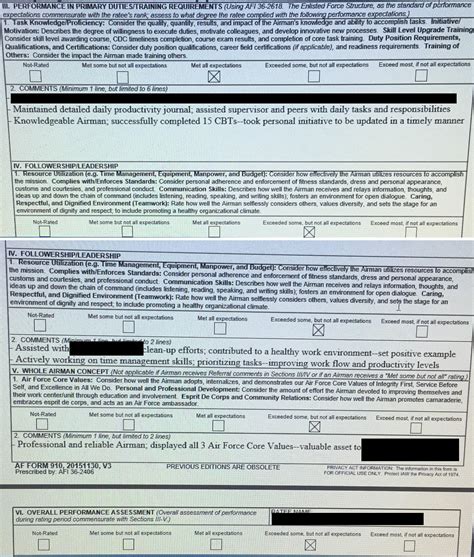
The United States Air Force (USAF) Evaluation and Performance Report (EPR) form is a critical document that assesses an airman's job performance, adherence to Air Force standards, and potential for advancement. Mastering the EPR form is essential for airmen to showcase their skills, accomplishments, and character, ultimately impacting their careers. In this article, we will provide you with 7 tips to help you master the USAF EPR form.

Understand the EPR Form Structure
The EPR form is a standardized document that consists of several sections, including:
- Section I: Airmen Information - Personal details, such as name, rank, and duty title.
- Section II: Performance Factors - Assessment of job performance, leadership, and adherence to Air Force standards.
- Section III: Performance Indicators - Measurement of performance in specific areas, such as productivity, quality of work, and teamwork.
- Section IV: Duty Description - Brief summary of the airman's job responsibilities.
- Section V: Performance Evaluation - Overall assessment of the airman's performance, including strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Section VI: Recommendations - Recommendations for future assignments, training, or promotion.
Understanding the EPR form structure is crucial to ensure that you provide accurate and relevant information.
Tip 1: Keep a Record of Your Accomplishments
Throughout the year, keep a record of your accomplishments, achievements, and contributions to your unit. This will help you to:
- Track your progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Provide specific examples of your performance in Section III: Performance Indicators.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
Use a journal, spreadsheet, or digital tool to record your accomplishments. Be specific and include dates, details, and outcomes.
Section II: Performance Factors - What to Focus On

Section II: Performance Factors is a critical section of the EPR form. It assesses your job performance, leadership, and adherence to Air Force standards. Focus on the following performance factors:
- Job Knowledge: Demonstrate your understanding of your job responsibilities and the Air Force's mission.
- Leadership: Showcase your leadership skills, including your ability to motivate and inspire your team.
- Adherence to Standards: Highlight your commitment to Air Force standards, including safety, security, and integrity.
Tip 2: Use the Air Force's Core Values as a Guide
The Air Force's core values - Integrity First, Service Before Self, and Excellence in All We Do - should guide your performance and behavior. Use these values to:
- Inspire your actions and decisions.
- Evaluate your performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
By embracing the Air Force's core values, you will demonstrate your commitment to the Air Force's mission and standards.
Section III: Performance Indicators - Measuring Your Performance

Section III: Performance Indicators measures your performance in specific areas, such as productivity, quality of work, and teamwork. Use this section to:
- Provide specific examples of your performance.
- Quantify your achievements, including numbers, percentages, and metrics.
- Highlight your strengths and accomplishments.
Tip 3: Use the SMART Criteria to Evaluate Your Performance
The SMART criteria - Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound - can help you evaluate your performance and set goals. Use the SMART criteria to:
- Set specific, measurable, and achievable goals.
- Evaluate your performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
By using the SMART criteria, you will ensure that your goals and performance are aligned with the Air Force's mission and standards.
Section IV: Duty Description - Briefly Summarize Your Job Responsibilities

Section IV: Duty Description requires a brief summary of your job responsibilities. Use this section to:
- Provide an overview of your job duties and responsibilities.
- Highlight your key tasks and functions.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
Tip 4: Use Action Verbs to Describe Your Job Responsibilities
Use action verbs, such as "manage," "coordinate," and "develop," to describe your job responsibilities. This will help you to:
- Clearly communicate your job duties and responsibilities.
- Highlight your key tasks and functions.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
Action verbs will help you to create a concise and effective duty description.
Section V: Performance Evaluation - Overall Assessment of Your Performance

Section V: Performance Evaluation requires an overall assessment of your performance. Use this section to:
- Provide an honest and objective evaluation of your performance.
- Highlight your strengths and accomplishments.
- Identify areas for improvement and provide recommendations for future development.
Tip 5: Be Honest and Objective in Your Performance Evaluation
Be honest and objective in your performance evaluation. Avoid bias and ensure that your evaluation is based on facts and evidence. Use this section to:
- Provide an accurate assessment of your performance.
- Highlight your strengths and accomplishments.
- Identify areas for improvement and provide recommendations for future development.
By being honest and objective, you will demonstrate your commitment to integrity and excellence.
Section VI: Recommendations - Future Assignments, Training, or Promotion

Section VI: Recommendations requires recommendations for future assignments, training, or promotion. Use this section to:
- Provide recommendations for future development and growth.
- Highlight your career goals and aspirations.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
Tip 6: Align Your Recommendations with Your Career Goals
Align your recommendations with your career goals and aspirations. Use this section to:
- Provide recommendations for future development and growth.
- Highlight your career goals and aspirations.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
By aligning your recommendations with your career goals, you will demonstrate your commitment to your career and the Air Force's mission.
Final Tip: Review and Edit Your EPR Form

Finally, review and edit your EPR form carefully. Ensure that:
- Your form is complete and accurate.
- Your performance factors, indicators, and evaluation are consistent.
- Your recommendations are aligned with your career goals.
Tip 7: Get Feedback from Your Supervisor or Mentor
Get feedback from your supervisor or mentor on your EPR form. Use their feedback to:
- Improve your performance and evaluation.
- Identify areas for improvement and provide recommendations for future development.
- Support your performance evaluation in Section V: Performance Evaluation.
By getting feedback from your supervisor or mentor, you will demonstrate your commitment to excellence and continuous improvement.
Now that you have mastered the USAF EPR form, you are ready to showcase your skills, accomplishments, and character. Remember to keep a record of your accomplishments, use the Air Force's core values as a guide, and be honest and objective in your performance evaluation.
Take action today and master the USAF EPR form. Share your thoughts and experiences with us in the comments section below.
FAQ Section:
What is the purpose of the USAF EPR form?
+The purpose of the USAF EPR form is to assess an airman's job performance, adherence to Air Force standards, and potential for advancement.
How often is the USAF EPR form completed?
+The USAF EPR form is typically completed annually, but it may be completed more frequently depending on the airman's performance and career goals.
What is the importance of the Air Force's core values in the EPR form?
+The Air Force's core values - Integrity First, Service Before Self, and Excellence in All We Do - are essential in the EPR form as they guide an airman's performance and behavior.