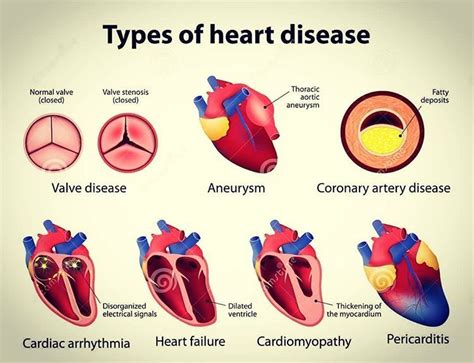
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. It is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, accounting for over 17.9 million deaths per year. In this article, we will delve into the top 5 forms of cardiovascular disease, exploring their definitions, symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Understanding Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease occurs when the heart and blood vessels are damaged, often due to a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. The condition can lead to a range of complications, including heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. While CVD is often associated with older adults, it can affect people of all ages, making it essential to understand the risks and take preventive measures.
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)

Coronary artery disease is the most common type of cardiovascular disease, accounting for over 370,000 deaths per year in the United States alone. CAD occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart, become narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup). This reduction in blood flow can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Symptoms of CAD may include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Causes of CAD include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Family history
Treatment options for CAD include:
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, stress management)
- Medications (statins, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors)
- Angioplasty or stenting
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
2. Heart Failure
Heart Failure

Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. This can occur due to a range of factors, including coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart valve problems. Heart failure can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, swelling, and shortness of breath.
Symptoms of heart failure may include:
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing or wheezing
Causes of heart failure include:
- Coronary artery disease
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Heart valve problems
- Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease)
Treatment options for heart failure include:
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, stress management)
- Medications (ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, diuretics)
- Device therapy (pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators)
- Heart transplantation
3. Stroke
Stroke

A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either due to a blockage (ischemic stroke) or a rupture (hemorrhagic stroke). This can lead to a range of symptoms, including weakness, numbness, and difficulty speaking.
Symptoms of stroke may include:
- Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision changes (double vision, blurred vision)
- Dizziness or loss of balance
Causes of stroke include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat)
Treatment options for stroke include:
- Emergency medical treatment (thrombectomy, thrombolysis)
- Rehabilitation therapy (physical, occupational, speech)
- Medications (anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents)
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, stress management)
4. Hypertension
Hypertension

Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is consistently too high. This can lead to a range of complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
Symptoms of hypertension may include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nosebleeds
- Fatigue
Causes of hypertension include:
- Family history
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- Excessive sodium intake
Treatment options for hypertension include:
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, stress management)
- Medications (diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers)
- Monitoring and follow-up care
5. Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation

Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat in which the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat too quickly and irregularly. This can lead to symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation may include:
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Causes of atrial fibrillation include:
- Age
- High blood pressure
- Heart valve problems
- Coronary artery disease
- Thyroid disease
Treatment options for atrial fibrillation include:
- Medications (anticoagulants, antiarrhythmics)
- Cardioversion (electric shock therapy)
- Ablation therapy
- Pacemaker implantation
In conclusion, cardiovascular disease is a complex and multifaceted condition that can manifest in different forms. By understanding the top 5 forms of CVD, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, stroke, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation, we can take steps to prevent and manage these conditions. If you are concerned about your heart health, consult with your healthcare provider and take proactive steps to reduce your risk.
What are the main causes of cardiovascular disease?
+The main causes of cardiovascular disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and family history.
Can cardiovascular disease be prevented?
+Yes, cardiovascular disease can be prevented by making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and quitting smoking.
What are the symptoms of coronary artery disease?
+The symptoms of coronary artery disease may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness or lightheadedness.