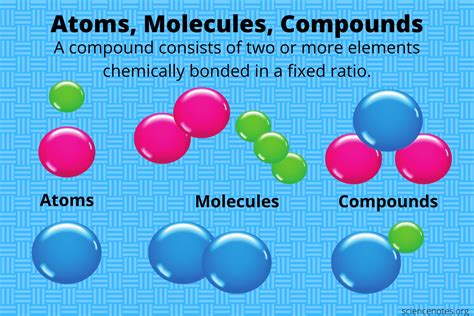
Elements are the building blocks of matter, and when they combine, they form compounds. This union is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and it's essential to understand how elements interact with each other to create new substances. In this article, we'll delve into the world of chemical bonding, exploring the different types of bonds, the factors that influence their formation, and the characteristics of compounds.
Chemical bonds are the attractive and repulsive forces that hold atoms together, forming a compound. There are several types of chemical bonds, including covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds. Covalent bonds are the most common type of bond and occur when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. Ionic bonds, on the other hand, form when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in a bond between two oppositely charged ions. Metallic bonds are a type of covalent bond that occurs between metal atoms, where electrons are shared among a lattice of metal ions.
How Elements Combine to Form Compounds

When elements combine to form compounds, they follow specific rules and guidelines. The first step in forming a compound is the interaction between two or more atoms. This interaction can occur through various means, such as sharing or transferring electrons. The resulting bond can be either strong or weak, depending on the type of bond and the elements involved.
One of the key factors that influence the formation of compounds is the electronegativity of the elements involved. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself. When two atoms with different electronegativities interact, the atom with the higher electronegativity tends to pull the shared electrons towards itself. This results in a polar covalent bond, where the electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms.
Factors That Influence the Formation of Compounds
In addition to electronegativity, several other factors influence the formation of compounds. These include:
- Atomic size: The size of the atoms involved can affect the formation of compounds. Larger atoms tend to form bonds more easily than smaller atoms.
- Valence electrons: The number of valence electrons an atom has can influence its ability to form bonds. Atoms with a full outer energy level tend to be less reactive than those with an incomplete outer energy level.
- Ionization energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom can affect its ability to form bonds. Atoms with low ionization energies tend to form bonds more easily than those with high ionization energies.
Types of Compounds

Compounds can be classified into several types, including:
- Molecular compounds: These compounds are formed when two or more atoms share electrons to form a covalent bond.
- Ionic compounds: These compounds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in a bond between two oppositely charged ions.
- Metallic compounds: These compounds are formed when metal atoms share electrons among a lattice of metal ions.
Characteristics of Compounds
Compounds have several characteristics that distinguish them from elements. These include:
- Chemical properties: Compounds have different chemical properties than the elements that make them up.
- Physical properties: Compounds have different physical properties than the elements that make them up, such as melting and boiling points.
- Composition: Compounds have a fixed composition, meaning that they are made up of a specific ratio of elements.
Importance of Compounds in Everyday Life

Compounds play a vital role in everyday life, and their importance cannot be overstated. They are used in a wide range of applications, from medicine to technology. Some examples of compounds that are essential to everyday life include:
- Water (H2O): A compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen, essential for human life.
- Salt (NaCl): A compound made up of sodium and chlorine, used as a seasoning and preservative.
- Ammonia (NH3): A compound made up of nitrogen and hydrogen, used as a fertilizer and cleaning agent.
Real-World Applications of Compounds
Compounds have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Medicine: Compounds are used to create medicines that can cure a wide range of diseases and conditions.
- Technology: Compounds are used in the production of electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones.
- Agriculture: Compounds are used as fertilizers and pesticides to improve crop yields and reduce pests.
Conclusion: A Union of Elements

In conclusion, the combination of elements to form compounds is a fundamental concept in chemistry. Understanding how elements interact with each other to create new substances is essential for understanding the world around us. Compounds have a wide range of applications, from medicine to technology, and their importance cannot be overstated. By exploring the world of chemical bonding, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex interactions that occur between elements and the compounds they form.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of how elements combine to form compounds. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread the word about the importance of compounds in everyday life.
What is a compound?
+A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements combine in a specific ratio.
What are the different types of chemical bonds?
+The three main types of chemical bonds are covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds.
What is electronegativity?
+Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself.