Graphing slope intercept form is a fundamental concept in algebra and mathematics. It is used to represent linear equations in a graphical format, making it easier to visualize and understand the relationship between variables. Mastering graphing slope intercept form can help you solve problems more efficiently and effectively. In this article, we will discuss five ways to master graphing slope intercept form.
Understanding the Basics of Slope Intercept Form
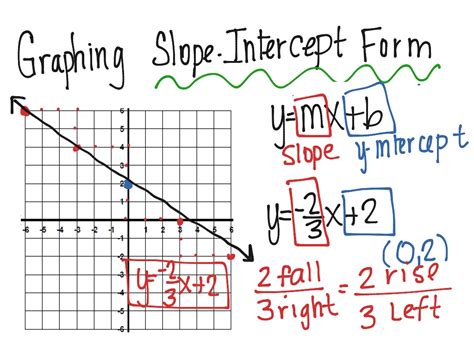
Before diving into the five ways to master graphing slope intercept form, it's essential to understand the basics. Slope intercept form is a linear equation written in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. The slope represents the rate of change of the line, and the y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis.

1. Visualizing the Slope and Y-Intercept
One of the most effective ways to master graphing slope intercept form is to visualize the slope and y-intercept. Imagine a line with a specific slope, and then identify the y-intercept. For example, if the equation is y = 2x + 3, the slope is 2, and the y-intercept is 3. Visualize a line with a slope of 2, and then mark the point (0, 3) as the y-intercept.
How to Visualize the Slope and Y-Intercept:
- Start by drawing the y-axis and marking the y-intercept.
- Draw a line with the specified slope, using the y-intercept as a reference point.
- Use a ruler or other straightedge to ensure the line is straight.
- Label the x and y axes to create a complete graph.
2. Using Online Graphing Tools
Another way to master graphing slope intercept form is to use online graphing tools. These tools allow you to input the equation and see the graph instantly. This can help you visualize the slope and y-intercept more easily, and make adjustments as needed. Some popular online graphing tools include Desmos, Graphing Calculator, and Mathway.

3. Practicing with Different Equations
Practice is key to mastering graphing slope intercept form. Try graphing different equations, varying the slope and y-intercept. This will help you develop a deeper understanding of how the slope and y-intercept affect the graph.
Examples of Equations to Practice:
- y = x + 2
- y = 2x - 3
- y = -x + 1
- y = x - 4
4. Creating a Table of Values
Creating a table of values is another effective way to master graphing slope intercept form. By plugging in different values for x and calculating the corresponding y-values, you can create a table of points that can be used to graph the line.
How to Create a Table of Values:
- Choose a range of x-values, such as -2, -1, 0, 1, and 2.
- Plug each x-value into the equation and calculate the corresponding y-value.
- Create a table with the x and y values.
- Use the table to graph the line.

5. Identifying Common Mistakes
Finally, it's essential to identify common mistakes when graphing slope intercept form. Some common mistakes include:
Common Mistakes to Watch Out For:
- Incorrectly identifying the slope or y-intercept.
- Failing to label the x and y axes.
- Graphing a line with the wrong slope or y-intercept.
- Not checking the graph for accuracy.
By following these five ways to master graphing slope intercept form, you can improve your understanding of linear equations and become more confident in your ability to graph them.

We hope this article has been helpful in your journey to master graphing slope intercept form. With practice and patience, you can become proficient in graphing linear equations and take your math skills to the next level.
What is slope intercept form?
+Slope intercept form is a linear equation written in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
How do I graph a slope intercept form equation?
+To graph a slope intercept form equation, start by drawing the y-axis and marking the y-intercept. Then, draw a line with the specified slope, using the y-intercept as a reference point.
What are some common mistakes to watch out for when graphing slope intercept form?
+Common mistakes to watch out for include incorrectly identifying the slope or y-intercept, failing to label the x and y axes, and graphing a line with the wrong slope or y-intercept.