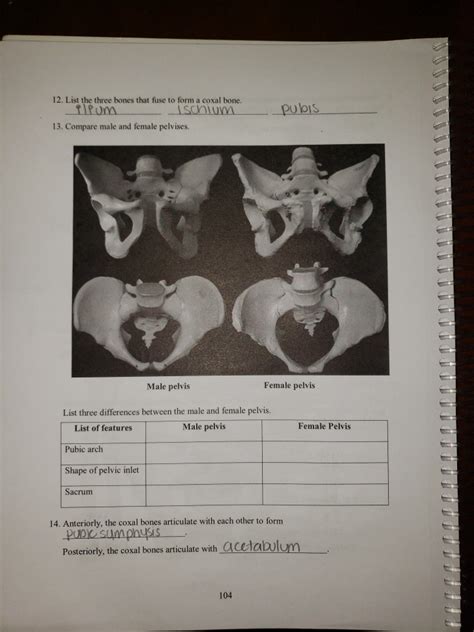
The coxal bone, also known as the hip bone, is a complex structure that forms the foundation of the pelvis. It is composed of three main bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis. These bones fuse together during childhood and adolescence to form a single, solid coxal bone. Understanding the process of coxal bone formation is essential for anatomists, orthopedic surgeons, and medical professionals. In this article, we will explore three ways to fuse and form the coxal bone.
The Importance of Coxal Bone Formation
Coxal bone formation is a critical process that affects the overall structure and function of the pelvis. A well-formed coxal bone provides a stable foundation for the pelvis, allowing for efficient movement and weight-bearing activities. Any abnormalities or defects in coxal bone formation can lead to various health issues, such as hip dysplasia, arthritis, or chronic pain.
The Role of Genetics in Coxal Bone Formation
Genetics play a significant role in coxal bone formation. Research has shown that genetic factors can influence the development and fusion of the coxal bone. For example, certain genetic mutations can affect the expression of genes involved in bone formation, leading to abnormalities in coxal bone development. Understanding the genetic factors that contribute to coxal bone formation can help researchers develop new treatments for related disorders.

Method 1: Endochondral Ossification
Endochondral ossification is the primary process by which the coxal bone forms. This process involves the replacement of cartilage templates with bone tissue. During embryonic development, the ilium, ischium, and pubis bones form as separate cartilage structures. As the fetus grows, these cartilage templates undergo endochondral ossification, where cartilage cells (chondrocytes) proliferate and differentiate into bone cells (osteoblasts). The bone cells then deposit bone matrix, gradually replacing the cartilage tissue.
Method 2: Intramembranous Ossification
Intramembranous ossification is another process that contributes to coxal bone formation. This process involves the direct transformation of mesenchymal cells into bone cells, without the formation of a cartilage template. During intramembranous ossification, mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts, which then deposit bone matrix to form bone tissue. This process occurs in the periosteum, a layer of connective tissue that surrounds the bone.
Method 3: Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is an ongoing process that involves the resorption and formation of bone tissue. During childhood and adolescence, bone remodeling plays a crucial role in shaping the coxal bone. Osteoclasts, specialized cells that break down bone tissue, resorb bone matrix, while osteoblasts deposit new bone tissue. This process of bone remodeling allows the coxal bone to adapt to changing loads and stresses, ensuring proper formation and function.
Understanding the Process of Coxal Bone Fusion
Coxal bone fusion is a complex process that involves the integration of multiple bones. The ilium, ischium, and pubis bones fuse together through a process called synostosis. During synostosis, the bones are connected by fibrous tissue, which gradually ossifies to form a solid bone.

Factors that Influence Coxal Bone Fusion
Several factors can influence coxal bone fusion, including:
- Genetics: Genetic mutations can affect the expression of genes involved in bone formation, leading to abnormalities in coxal bone fusion.
- Hormones: Hormonal changes during puberty can influence bone growth and development, affecting coxal bone fusion.
- Nutrition: Adequate nutrition, particularly calcium and vitamin D, is essential for proper bone growth and development.
The Role of Orthopedic Surgery in Coxal Bone Formation
Orthopedic surgery plays a crucial role in treating disorders related to coxal bone formation. Surgeons use various techniques, such as osteotomy and bone grafting, to correct abnormalities in coxal bone formation. Understanding the process of coxal bone formation is essential for orthopedic surgeons to develop effective treatment plans.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the formation of the coxal bone is a complex process that involves multiple bones and tissues. Understanding the three ways to fuse and form the coxal bone – endochondral ossification, intramembranous ossification, and bone remodeling – is essential for anatomists, orthopedic surgeons, and medical professionals. By recognizing the factors that influence coxal bone formation, researchers and clinicians can develop new treatments for related disorders.

Share Your Thoughts
We would love to hear from you! Share your thoughts on the importance of coxal bone formation and its relevance to orthopedic surgery. Do you have any questions or comments about the article? Please leave a comment below.
What is the coxal bone?
+The coxal bone, also known as the hip bone, is a complex structure that forms the foundation of the pelvis. It is composed of three main bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
What are the three ways to fuse and form the coxal bone?
+The three ways to fuse and form the coxal bone are endochondral ossification, intramembranous ossification, and bone remodeling.
What is the role of genetics in coxal bone formation?
+Genetics play a significant role in coxal bone formation. Research has shown that genetic factors can influence the development and fusion of the coxal bone.