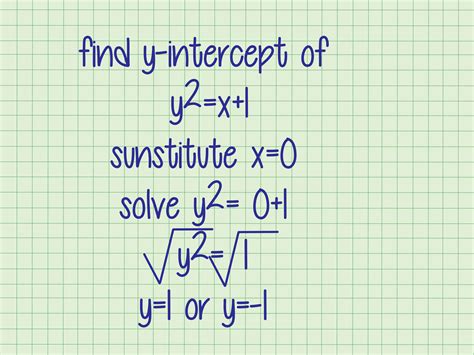Finding the y-intercept of a linear equation is a fundamental concept in algebra and graphing. The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis, and it's essential to understand how to find it from the standard form of a linear equation. In this article, we'll explore three ways to find the y-intercept from the standard form, along with examples, explanations, and visual aids.
Understanding the Standard Form of a Linear Equation

The standard form of a linear equation is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are constants, and x and y are variables. The standard form is also known as the general form, and it's a useful way to represent linear equations.
Method 1: Isolating y
One way to find the y-intercept from the standard form is to isolate y. To do this, we need to move the x term to the other side of the equation and then simplify.
Example:
2x + 3y = 6
To find the y-intercept, we can isolate y by subtracting 2x from both sides of the equation:
3y = -2x + 6
Next, we can divide both sides of the equation by 3 to solve for y:
y = (-2/3)x + 2
The y-intercept is the value of y when x is 0. In this case, the y-intercept is 2.
Using the Slope-Intercept Form

Another way to find the y-intercept from the standard form is to convert the equation to the slope-intercept form, which is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
Example:
x - 2y = 4
To convert this equation to the slope-intercept form, we can add 2y to both sides of the equation:
x = 2y + 4
Next, we can subtract x from both sides of the equation and then divide both sides by 2:
y = (1/2)x - 2
The y-intercept is the value of y when x is 0. In this case, the y-intercept is -2.
Method 3: Graphing
A third way to find the y-intercept from the standard form is to graph the equation. To do this, we can plot two points on the graph and then draw a line through them.
Example:
3x + 2y = 6
To graph this equation, we can plot the points (0, 3) and (2, 0). The line that passes through these points is the graph of the equation.

The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis. In this case, the y-intercept is 3.
Conclusion
Finding the y-intercept from the standard form of a linear equation is a crucial skill in algebra and graphing. In this article, we explored three ways to find the y-intercept from the standard form: isolating y, using the slope-intercept form, and graphing. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific problem and the student's preferences.
By mastering these three methods, students can develop a deeper understanding of linear equations and improve their problem-solving skills.
What is the y-intercept of a linear equation?
+The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
How do I find the y-intercept from the standard form?
+There are three ways to find the y-intercept from the standard form: isolating y, using the slope-intercept form, and graphing.
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
+The slope-intercept form is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.