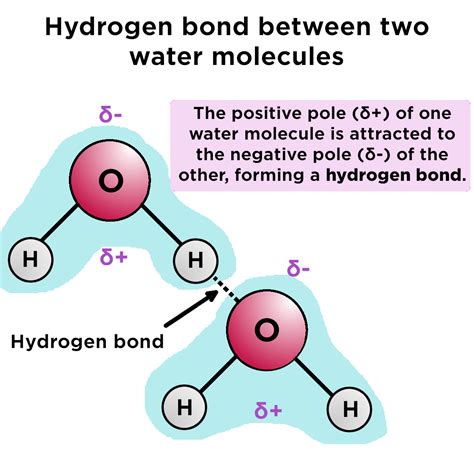
Hydrogen bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry, playing a crucial role in the behavior and properties of molecules. It is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. These bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds, but they are essential for understanding the structure and properties of many substances.

Hydrogen bonds are responsible for the unique properties of water, such as its high boiling point and surface tension. They also play a crucial role in the structure and function of biomolecules, such as DNA and proteins. In this article, we will explore the concept of hydrogen bonding in more detail, discussing the molecules that form these bonds and the factors that influence their strength.
What is Hydrogen Bonding?
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom. This electronegative atom pulls the shared electrons closer to itself, creating a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom. This partial positive charge is attracted to a partial negative charge on another molecule, resulting in a weak electrostatic attraction.
The strength of a hydrogen bond depends on the electronegativity of the atom bonded to the hydrogen and the distance between the molecules. Hydrogen bonds are typically weaker than covalent bonds, but stronger than other types of intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces.
Types of Hydrogen Bonds
There are two main types of hydrogen bonds: intramolecular and intermolecular. Intramolecular hydrogen bonds occur within a single molecule, while intermolecular hydrogen bonds occur between two or more molecules.
Intramolecular hydrogen bonds are important in the structure and function of biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA. These bonds help to stabilize the molecule and determine its three-dimensional structure.
Intermolecular hydrogen bonds, on the other hand, are responsible for the physical properties of substances, such as their boiling point and surface tension.
Molecules that Form Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds can form between a wide range of molecules, including:
- Water (H2O)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Methanol (CH3OH)
- Hydrogen fluoride (HF)
- Carboxylic acids (RCOOH)
- Amines (RNH2)
- Alcohols (ROH)
These molecules all have a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, which creates a partial positive charge on the hydrogen. This partial positive charge is attracted to a partial negative charge on another molecule, resulting in a hydrogen bond.

Factors that Influence Hydrogen Bonding
Several factors can influence the strength of hydrogen bonds, including:
- Electronegativity of the atom bonded to the hydrogen
- Distance between the molecules
- Temperature
- Pressure
The electronegativity of the atom bonded to the hydrogen is the most important factor in determining the strength of a hydrogen bond. Atoms with high electronegativity, such as oxygen and fluorine, create a stronger partial positive charge on the hydrogen, resulting in a stronger hydrogen bond.
The distance between the molecules is also important, as hydrogen bonds are strongest when the molecules are close together. Temperature and pressure can also affect the strength of hydrogen bonds, with higher temperatures and pressures typically weakening the bonds.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding plays a crucial role in many areas of chemistry and biology. Some of the importance of hydrogen bonding includes:
- Structure and function of biomolecules
- Physical properties of substances
- Chemical reactions and catalysis
- Biological processes, such as protein folding and DNA replication
Hydrogen bonding is essential for understanding the behavior and properties of many substances, from the structure of biomolecules to the physical properties of water.

Applications of Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding has many practical applications in fields such as:
- Materials science
- Biotechnology
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Food industry
Understanding hydrogen bonding is essential for developing new materials and technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells and biomimetic surfaces.
Conclusion
Hydrogen bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry, playing a crucial role in the behavior and properties of molecules. Understanding the molecules that form hydrogen bonds and the factors that influence their strength is essential for many areas of chemistry and biology. From the structure of biomolecules to the physical properties of substances, hydrogen bonding is a vital aspect of chemistry that continues to inspire new research and discoveries.

We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions about hydrogen bonding in the comments below. What do you think is the most important aspect of hydrogen bonding? How do you think it can be applied in real-world scenarios?
What is hydrogen bonding?
+Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom.
Which molecules form hydrogen bonds?
+Molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, can form hydrogen bonds.
What is the importance of hydrogen bonding?
+Hydrogen bonding plays a crucial role in many areas of chemistry and biology, including the structure and function of biomolecules, physical properties of substances, and biological processes.