Fluorine is a highly reactive gas that readily forms covalent bonds with many elements. In fact, fluorine is so reactive that it forms compounds with almost every element in the periodic table, including noble gases like xenon and krypton. One of the elements that forms covalent bonds with fluorine is carbon.
Carbon and fluorine form a covalent bond in a class of compounds known as fluorocarbons. Fluorocarbons are used in a wide range of applications, including refrigeration, air conditioning, and as propellants in aerosol cans. The covalent bond between carbon and fluorine is very strong, which makes fluorocarbons extremely stable and resistant to chemical reactions.
Another element that forms covalent bonds with fluorine is hydrogen. Hydrogen and fluorine form a covalent bond in a compound known as hydrogen fluoride (HF). Hydrogen fluoride is a highly reactive gas that is used in the production of fluorocarbons, as well as in the manufacture of aluminum and stainless steel.
Other elements that form covalent bonds with fluorine include nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur. These elements form a range of compounds, including fluoramines, fluorates, and fluorides, which have a wide range of applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and industry.

What is a Covalent Bond?
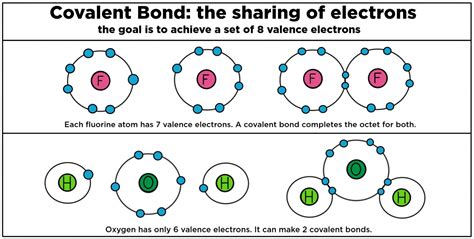
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two or more atoms when they share one or more pairs of electrons. Covalent bonds are typically found in molecules, where they hold the atoms together in a fixed arrangement. Covalent bonds are strong and stable, and they are responsible for the structure and properties of molecules.
Covalent bonds are different from ionic bonds, which form between atoms that have opposite charges. In an ionic bond, one atom loses an electron to become a positively charged ion, while another atom gains an electron to become a negatively charged ion. The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other, forming a strong and stable bond.
Covalent bonds, on the other hand, form when atoms share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level. This sharing of electrons is typically found in molecules, where the atoms are bonded together in a fixed arrangement.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are several types of covalent bonds, including:
- Sigma bonds: These are the strongest type of covalent bond and form when two atoms share a pair of electrons in a symmetrical arrangement.
- Pi bonds: These are weaker than sigma bonds and form when two atoms share a pair of electrons in a parallel arrangement.
- Double bonds: These form when two atoms share two pairs of electrons.
- Triple bonds: These form when two atoms share three pairs of electrons.
Covalent bonds can also be classified as polar or nonpolar. Polar covalent bonds form when the electrons are shared unequally between the atoms, resulting in a molecule with a positive and negative end. Nonpolar covalent bonds form when the electrons are shared equally between the atoms, resulting in a molecule with no net charge.

Properties of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds have several properties that are important in chemistry, including:
- Bond length: The distance between the atoms in a covalent bond.
- Bond strength: The energy required to break a covalent bond.
- Bond polarity: The distribution of electrons in a covalent bond.
- Bond angle: The angle between the atoms in a covalent bond.
Covalent bonds also have several advantages, including:
- High strength: Covalent bonds are typically strong and stable.
- Low reactivity: Covalent bonds are less reactive than ionic bonds.
- High melting and boiling points: Covalent bonds typically have high melting and boiling points.
However, covalent bonds also have several disadvantages, including:
- Low solubility: Covalent bonds can make molecules insoluble in water.
- Low conductivity: Covalent bonds can make molecules poor conductors of electricity.

Applications of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds have a wide range of applications in fields such as:
- Medicine: Covalent bonds are used in the development of pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- Agriculture: Covalent bonds are used in the development of pesticides and fertilizers.
- Industry: Covalent bonds are used in the manufacture of plastics, fibers, and other materials.
Covalent bonds are also used in the development of new materials and technologies, such as:
- Nanotechnology: Covalent bonds are used to create nanoparticles and nanomaterials.
- Biotechnology: Covalent bonds are used to create bioproducts and biomaterials.
- Energy storage: Covalent bonds are used to create batteries and other energy storage devices.

We hope this article has helped you understand which element forms covalent bonds with fluorine and the properties and applications of covalent bonds. Do you have any questions or comments? Please feel free to share them below.
What is a covalent bond?
+A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two or more atoms when they share one or more pairs of electrons.
What are the properties of covalent bonds?
+Covalent bonds have several properties, including bond length, bond strength, bond polarity, and bond angle.
What are the applications of covalent bonds?
+Covalent bonds have a wide range of applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, industry, and energy storage.