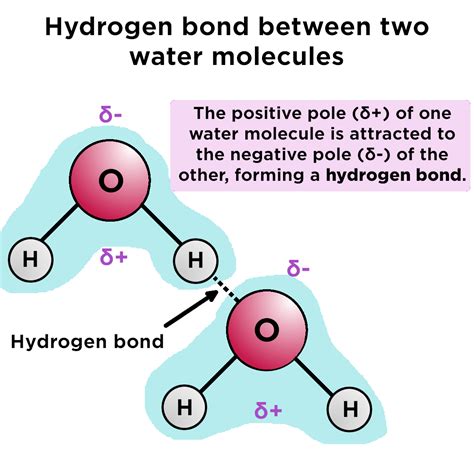
Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that plays a crucial role in the physical and chemical properties of molecules. These bonds are responsible for the structure and function of many biological molecules, such as DNA, proteins, and water. In this article, we will explore the molecules that form hydrogen bonds, their characteristics, and the importance of these bonds in various biological processes.
Hydrogen bonds are formed between molecules that have a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. This electronegative atom pulls the shared electrons closer to itself, creating a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom. This partial positive charge is attracted to the partial negative charge on another electronegative atom, resulting in a weak electrostatic attraction between the two molecules.

Characteristics of Molecules That Form Hydrogen Bonds
Molecules that form hydrogen bonds typically have the following characteristics:
- A hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
- A high degree of polarity, resulting in a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the electronegative atom.
- A relatively small size, allowing for close approach between molecules and increasing the strength of the hydrogen bond.
Some examples of molecules that form hydrogen bonds include:
- Water (H2O)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Methanol (CH3OH)
- Hydrogen fluoride (HF)
- DNA and RNA nucleotides
Water: A Unique Molecule
Water is one of the most common molecules that form hydrogen bonds. Its unique structure, with two hydrogen atoms bonded to a single oxygen atom, allows it to form strong hydrogen bonds with other water molecules. This results in a high boiling point and surface tension, making water an essential component of many biological systems.

Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Biological Systems
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in many biological systems, including:
- DNA structure and replication: Hydrogen bonds between nucleotides hold the double helix structure of DNA together, allowing for the transmission of genetic information.
- Protein structure and function: Hydrogen bonds between amino acids help to stabilize the three-dimensional structure of proteins, allowing them to perform specific biological functions.
- Cell membrane structure: Hydrogen bonds between phospholipid molecules help to maintain the integrity of cell membranes, regulating the movement of molecules in and out of cells.
Hydrogen Bonds in DNA Replication
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the replication of DNA. During replication, the double helix structure of DNA is unwound, and the nucleotides are paired with their complementary bases. Hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides hold the new DNA strands together, allowing for the accurate transmission of genetic information.

Factors That Affect Hydrogen Bond Strength
Several factors can affect the strength of hydrogen bonds, including:
- Distance between molecules: The closer the molecules are, the stronger the hydrogen bond.
- Electronegativity of the atoms involved: The more electronegative the atoms, the stronger the hydrogen bond.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures can disrupt hydrogen bonds, making them weaker.
- Solvent effects: The presence of certain solvents, such as water or methanol, can affect the strength of hydrogen bonds.
Temperature Effects on Hydrogen Bonds
Temperature can have a significant effect on the strength of hydrogen bonds. At higher temperatures, the molecules have more kinetic energy, making it easier for them to break free from the weak electrostatic attraction of the hydrogen bond. This can result in the disruption of biological structures, such as the denaturation of proteins or the melting of DNA.

Applications of Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds have many applications in various fields, including:
- Biotechnology: Hydrogen bonds are used in biotechnology to develop new therapeutic agents and diagnostic tools.
- Materials science: Hydrogen bonds are used in materials science to develop new materials with unique properties.
- Pharmaceutical industry: Hydrogen bonds are used in the pharmaceutical industry to develop new drugs and drug delivery systems.
Hydrogen Bonds in Biotechnology
Hydrogen bonds are used in biotechnology to develop new therapeutic agents and diagnostic tools. For example, hydrogen bonds are used to design new protein structures with specific biological functions. Additionally, hydrogen bonds are used to develop new diagnostic tools, such as biosensors and biochips.

In conclusion, hydrogen bonds are a crucial type of intermolecular force that plays a vital role in many biological systems. Molecules that form hydrogen bonds have specific characteristics, such as a high degree of polarity and a relatively small size. Hydrogen bonds are essential for the structure and function of many biological molecules, including DNA, proteins, and water. Understanding the characteristics and applications of hydrogen bonds is essential for advancing our knowledge of biological systems and developing new technologies.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and comments on this article. What do you think is the most significant application of hydrogen bonds? Share your ideas and let's continue the conversation!
What is a hydrogen bond?
+A hydrogen bond is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules that have a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
What are the characteristics of molecules that form hydrogen bonds?
+Molecules that form hydrogen bonds typically have a high degree of polarity, resulting in a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the electronegative atom.
What is the importance of hydrogen bonds in biological systems?
+Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in many biological systems, including DNA structure and replication, protein structure and function, and cell membrane structure.