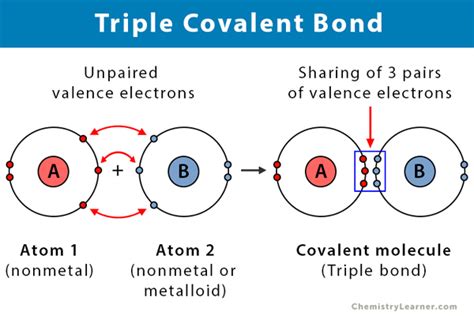
The world of chemistry is full of fascinating phenomena, and one of the most intriguing is the formation of triple covalent bonds. These bonds are a crucial aspect of molecular structure and are responsible for the unique properties of certain compounds. But what elements are capable of forming these strong and stable bonds?
In this article, we will delve into the world of triple covalent bonds and explore the three elements that are known to form them. We will also discuss the mechanisms behind their formation and provide examples of compounds that exhibit these bonds.
What are Triple Covalent Bonds?

Before we dive into the elements that form triple covalent bonds, let's first understand what these bonds are. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that forms between two atoms when they share one or more pairs of electrons. Triple covalent bonds are a type of covalent bond where three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. This results in a strong and stable bond that is characteristic of certain compounds.
Element 1: Carbon (C)

Carbon is one of the most well-known elements that form triple covalent bonds. It is a fundamental element in organic chemistry and is found in a wide range of compounds, including alkenes, alkynes, and aromatics. Carbon's ability to form triple covalent bonds is due to its unique electronic configuration, which allows it to form a linear geometry with three bonds.
One of the most common examples of a compound that exhibits a triple covalent bond is acetylene (C2H2). This compound is a simple alkyne that consists of two carbon atoms bonded together with a triple covalent bond.
How Carbon Forms Triple Covalent Bonds
Carbon forms triple covalent bonds through a process called hybridization. In this process, the carbon atom's 2s and 2p orbitals are mixed to form three equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are oriented in a linear geometry and are capable of forming three bonds with other atoms.
Element 2: Nitrogen (N)

Nitrogen is another element that is capable of forming triple covalent bonds. It is a fundamental element in many biomolecules, including amino acids and nucleotides. Nitrogen's ability to form triple covalent bonds is due to its electronic configuration, which allows it to form a linear geometry with three bonds.
One of the most common examples of a compound that exhibits a triple covalent bond is cyanide (CN-). This compound is a simple anion that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to a carbon atom with a triple covalent bond.
How Nitrogen Forms Triple Covalent Bonds
Nitrogen forms triple covalent bonds through a process called hybridization. In this process, the nitrogen atom's 2s and 2p orbitals are mixed to form three equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are oriented in a linear geometry and are capable of forming three bonds with other atoms.
Element 3: Phosphorus (P)

Phosphorus is the third element that is capable of forming triple covalent bonds. It is a fundamental element in many biomolecules, including DNA and ATP. Phosphorus's ability to form triple covalent bonds is due to its electronic configuration, which allows it to form a linear geometry with three bonds.
One of the most common examples of a compound that exhibits a triple covalent bond is phosphorus trifluoride (PF3). This compound is a simple molecule that consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to three fluorine atoms with single covalent bonds.
How Phosphorus Forms Triple Covalent Bonds
Phosphorus forms triple covalent bonds through a process called hybridization. In this process, the phosphorus atom's 3s and 3p orbitals are mixed to form three equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are oriented in a linear geometry and are capable of forming three bonds with other atoms.
Conclusion: The Importance of Triple Covalent Bonds
Triple covalent bonds are a crucial aspect of molecular structure and are responsible for the unique properties of certain compounds. The three elements that are capable of forming these bonds - carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus - are fundamental to many biomolecules and are responsible for their structure and function.
In conclusion, triple covalent bonds are an important aspect of chemistry that are worth exploring further. By understanding the mechanisms behind their formation and the elements that are capable of forming them, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of molecular structure.
What are triple covalent bonds?
+Triple covalent bonds are a type of covalent bond where three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms.
Which elements are capable of forming triple covalent bonds?
+The three elements that are capable of forming triple covalent bonds are carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
What is the importance of triple covalent bonds in molecular structure?
+Triple covalent bonds are responsible for the unique properties of certain compounds and are fundamental to many biomolecules.