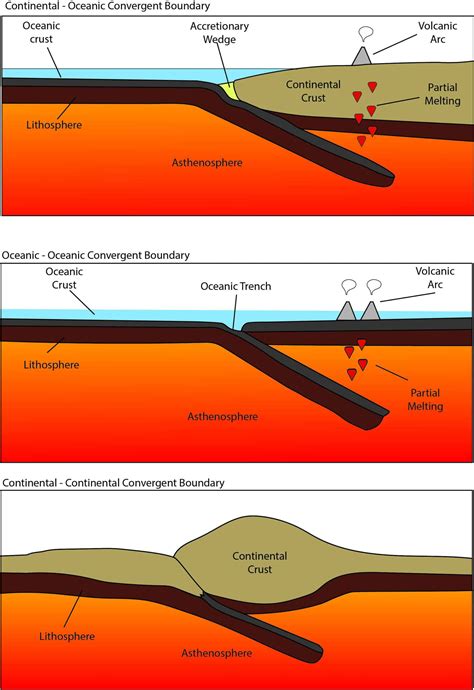
The Earth's lithosphere is broken into several large plates that move relative to each other, creating boundaries where they interact. Convergent boundaries, where two plates move towards each other, are particularly interesting as they can lead to the formation of mountain ranges. In this article, we will explore three types of mountain ranges that can form at convergent boundaries.
The process of mountain building at convergent boundaries involves the collision of two plates, resulting in the formation of mountains as the Earth's crust is compressed and thickened. This process can occur through various mechanisms, including subduction, continental collision, and oceanic-continental convergence.
1. Fold Mountains

Fold mountains are formed when two continental plates collide, causing the Earth's crust to buckle and fold. This process can result in the formation of long, narrow mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas or the Rocky Mountains. The folding of the Earth's crust can lead to the creation of faults, fractures, and folds, which can be thousands of feet high.
Fold mountains can be further divided into two subtypes: symmetrical folds and asymmetrical folds. Symmetrical folds occur when the two colliding plates have similar thickness and composition, resulting in a symmetrical fold pattern. Asymmetrical folds, on the other hand, occur when the two plates have different thickness and composition, resulting in an asymmetrical fold pattern.
Examples of Fold Mountains
- The Himalayas, formed as a result of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates
- The Rocky Mountains, formed as a result of the collision between the North American and Pacific plates
- The Andes mountain range, formed as a result of the collision between the South American and Nazca plates
2. Volcanic Arcs

Volcanic arcs are formed when an oceanic plate is subducted beneath a continental plate, resulting in the formation of a chain of volcanoes. As the oceanic plate sinks into the Earth's mantle, it encounters increasing heat and pressure, causing the rocks to melt and form magma. This magma then rises to the surface, resulting in volcanic activity.
Volcanic arcs can be found at the boundary between an oceanic and continental plate, such as the Pacific Ring of Fire. They can also be found at the boundary between two oceanic plates, such as the Mariana Arc.
Examples of Volcanic Arcs
- The Pacific Ring of Fire, a chain of volcanoes that surrounds the Pacific Ocean
- The Mariana Arc, a chain of volcanoes that stretches from Japan to the Mariana Islands
- The Andean Volcanic Arc, a chain of volcanoes that stretches along the western edge of South America
3. Block-Faulted Mountains

Block-faulted mountains are formed when large blocks of the Earth's crust are pushed upwards along faults, resulting in the formation of mountains. This process can occur at convergent boundaries, where the collision of two plates results in the formation of faults and fractures.
Block-faulted mountains can be found in areas where the Earth's crust has been stretched and thinned, such as in the Basin and Range Province of North America. They can also be found in areas where the Earth's crust has been compressed and thickened, such as in the Himalayas.
Examples of Block-Faulted Mountains
- The Sierra Nevada mountain range, formed as a result of block faulting in the Basin and Range Province
- The Appalachian Mountains, formed as a result of block faulting in eastern North America
- The Transantarctic Mountains, formed as a result of block faulting in Antarctica
In conclusion, convergent boundaries can lead to the formation of three types of mountain ranges: fold mountains, volcanic arcs, and block-faulted mountains. Each of these types of mountain ranges has unique characteristics and is formed through different mechanisms. Understanding the processes that shape our planet's surface is essential for appreciating the beauty and complexity of mountain ranges.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the three types of mountain ranges formed at convergent boundaries. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to ask. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and family.
What is a convergent boundary?
+A convergent boundary is a boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving towards each other. This can result in the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
What is the difference between a fold mountain and a volcanic arc?
+A fold mountain is formed through the folding of the Earth's crust, resulting in the creation of mountains. A volcanic arc, on the other hand, is formed through the subduction of an oceanic plate beneath a continental plate, resulting in the formation of a chain of volcanoes.
What is block faulting?
+Block faulting is a process where large blocks of the Earth's crust are pushed upwards along faults, resulting in the formation of mountains.