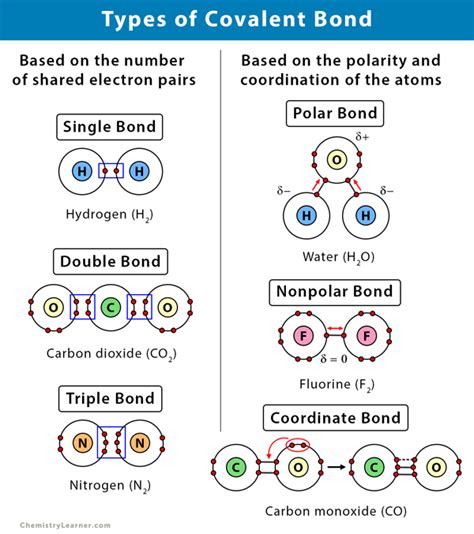
Covalent bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and they play a crucial role in the formation of molecules. Atoms that form covalent bonds share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. In this article, we will explore five types of atoms that form covalent bonds, their characteristics, and examples of compounds they form.

1. Hydrogen Atoms
Hydrogen atoms are the lightest and most abundant atoms in the universe. They have one electron in their outermost energy level, which makes them highly reactive. Hydrogen atoms form covalent bonds with other atoms by sharing their single electron. This type of bond is known as a sigma (σ) bond.
Hydrogen atoms can form covalent bonds with a variety of atoms, including oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon. For example, hydrogen and oxygen atoms form a covalent bond to create water (H2O), while hydrogen and nitrogen atoms form a covalent bond to create ammonia (NH3).

Characteristics of Hydrogen Atoms
- Atomic number: 1
- Atomic mass: 1.00794 u
- Electron configuration: 1s1
- Highly reactive due to single electron in outermost energy level
2. Oxygen Atoms
Oxygen atoms are highly reactive and form covalent bonds with many other atoms. They have six electrons in their outermost energy level, which makes them tend to gain two electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. Oxygen atoms form covalent bonds with hydrogen, carbon, and other atoms to create a variety of compounds.
For example, oxygen and hydrogen atoms form a covalent bond to create water (H2O), while oxygen and carbon atoms form a covalent bond to create carbon dioxide (CO2).

Characteristics of Oxygen Atoms
- Atomic number: 8
- Atomic mass: 15.9994 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p4
- Highly reactive due to six electrons in outermost energy level
3. Nitrogen Atoms
Nitrogen atoms are highly abundant in the atmosphere and form covalent bonds with many other atoms. They have five electrons in their outermost energy level, which makes them tend to gain three electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. Nitrogen atoms form covalent bonds with hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon atoms to create a variety of compounds.
For example, nitrogen and hydrogen atoms form a covalent bond to create ammonia (NH3), while nitrogen and oxygen atoms form a covalent bond to create nitric oxide (NO).

Characteristics of Nitrogen Atoms
- Atomic number: 7
- Atomic mass: 14.0067 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p3
- Highly reactive due to five electrons in outermost energy level
4. Carbon Atoms
Carbon atoms are the basis of all life on Earth and form covalent bonds with many other atoms. They have four electrons in their outermost energy level, which makes them tend to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. Carbon atoms form covalent bonds with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other atoms to create a variety of compounds.
For example, carbon and hydrogen atoms form a covalent bond to create methane (CH4), while carbon and oxygen atoms form a covalent bond to create carbon dioxide (CO2).

Characteristics of Carbon Atoms
- Atomic number: 6
- Atomic mass: 12.011 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p2
- Forms four covalent bonds with other atoms
5. Fluorine Atoms
Fluorine atoms are highly reactive and form covalent bonds with many other atoms. They have seven electrons in their outermost energy level, which makes them tend to gain one electron to achieve a stable electronic configuration. Fluorine atoms form covalent bonds with hydrogen, carbon, and other atoms to create a variety of compounds.
For example, fluorine and hydrogen atoms form a covalent bond to create hydrogen fluoride (HF), while fluorine and carbon atoms form a covalent bond to create fluoromethane (CH3F).

Characteristics of Fluorine Atoms
- Atomic number: 9
- Atomic mass: 18.9984 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p5
- Highly reactive due to seven electrons in outermost energy level
In conclusion, covalent bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and they play a crucial role in the formation of molecules. The five types of atoms that form covalent bonds discussed in this article are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and fluorine. Each of these atoms has unique characteristics that make them highly reactive and able to form covalent bonds with other atoms.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of covalent bonds and the atoms that form them. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is a covalent bond?
+A covalent bond is a chemical bond that forms when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
Which atoms are most likely to form covalent bonds?
+Atoms that have a high number of electrons in their outermost energy level, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine, are most likely to form covalent bonds.
What is the difference between a covalent bond and an ionic bond?
+A covalent bond forms when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, while an ionic bond forms when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.