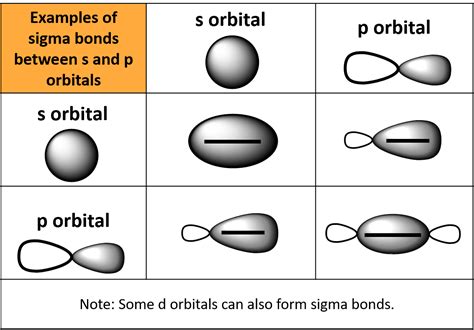
In the fascinating realm of chemistry, understanding the intricacies of molecular bonds is crucial for grasping the structure and behavior of molecules. Among the various types of bonds, sigma (σ) bonds play a pivotal role in forming the backbone of molecules. Sigma bonds are a type of covalent bond that is symmetrical about the bond axis, resulting in a cylindrical shape. The formation of sigma bonds involves the overlap of atomic orbitals, specifically two types that are central to this process: s-orbitals and p-orbitals.

Understanding Atomic Orbitals
Before diving into the specifics of sigma bond formation, it's essential to understand the nature of atomic orbitals. Atomic orbitals are mathematical descriptions of the regions around an atom where an electron is likely to be found. They come in various shapes and sizes, including s-orbitals, p-orbitals, d-orbitals, and f-orbitals. Each type of orbital has a unique geometry and can accommodate a specific number of electrons.
s-Orbitals
s-Orbitals are spherical in shape and symmetrical about the nucleus. They are the simplest type of orbital and can accommodate up to two electrons. s-Orbitals are further divided into different energy levels, such as 1s, 2s, 3s, and so on. The 1s orbital is the lowest energy level and is closest to the nucleus.

p-Orbitals
p-Orbitals are dumbbell-shaped and oriented along the x, y, and z axes. They can accommodate up to six electrons and are further divided into different energy levels, such as 2p, 3p, and so on. p-Orbitals are more complex than s-orbitals and have different orientations in space.

Formation of Sigma Bonds
Sigma bonds are formed when two atomic orbitals overlap end-to-end, resulting in a cylindrical shape. This type of overlap is known as head-on overlap. The formation of sigma bonds involves the overlap of s-orbitals and p-orbitals.
s-s Overlap
When two s-orbitals overlap, they form a sigma bond. This type of overlap is symmetrical about the bond axis and results in a strong and stable bond.

s-p Overlap
When an s-orbital overlaps with a p-orbital, they form a sigma bond. This type of overlap is also symmetrical about the bond axis and results in a strong and stable bond.

p-p Overlap
When two p-orbitals overlap, they form a sigma bond. This type of overlap is also symmetrical about the bond axis and results in a strong and stable bond.

Importance of Sigma Bonds
Sigma bonds play a crucial role in the formation of molecules. They are responsible for the strength and stability of molecules, and their formation is essential for understanding the structure and behavior of molecules.

Conclusion
In conclusion, sigma bonds are a type of covalent bond that is symmetrical about the bond axis. The formation of sigma bonds involves the overlap of atomic orbitals, specifically s-orbitals and p-orbitals. Understanding the nature of sigma bonds and their formation is essential for grasping the structure and behavior of molecules.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions about sigma bonds in the comments section below. Don't forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues who might find it informative and helpful.
What are sigma bonds?
+Sigma bonds are a type of covalent bond that is symmetrical about the bond axis.
What types of orbitals form sigma bonds?
+s-Orbitals and p-orbitals form sigma bonds.
What is the importance of sigma bonds?
+Sigma bonds play a crucial role in the formation of molecules and are responsible for their strength and stability.