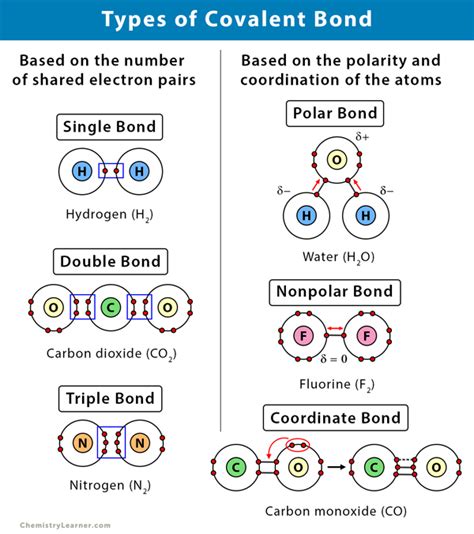
Covalent bonds are a fundamental aspect of chemistry, playing a crucial role in the formation of molecules. In this article, we will delve into the world of covalent bonds, exploring what elements form them, how they are created, and their significance in the world of chemistry.
Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. This sharing of electrons leads to the formation of a stable molecule, where the atoms are held together by the attractive forces between the electrons and the nuclei. Covalent bonds are typically found in molecules composed of non-metal atoms, such as carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen.

What Elements Form Covalent Bonds?
Covalent bonds can be formed between a wide range of elements, but they are most commonly found in molecules composed of non-metal atoms. Some of the most common elements that form covalent bonds include:
- Carbon (C)
- Oxygen (O)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Fluorine (F)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Hydrogen (H)
These elements are able to form covalent bonds due to their electron configuration. Non-metal atoms typically have a full outer energy level, which means they have a full set of electrons in their outermost energy level. This full outer energy level makes it difficult for the atoms to lose or gain electrons, leading to the formation of covalent bonds.
Electronegativity and Covalent Bonds
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. Atoms with high electronegativity values tend to attract electrons more strongly, leading to a greater degree of electron sharing in covalent bonds. Some of the most electronegative elements include:
- Fluorine (F)
- Oxygen (O)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Chlorine (Cl)
These elements tend to form covalent bonds with other atoms that have lower electronegativity values. For example, fluorine tends to form covalent bonds with hydrogen, which has a relatively low electronegativity value.

How Are Covalent Bonds Created?
Covalent bonds are created when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons leads to the formation of a stable molecule, where the atoms are held together by the attractive forces between the electrons and the nuclei.
There are several ways in which covalent bonds can be created, including:
- Atomic collisions: When two atoms collide, they can share electrons and form a covalent bond.
- Chemical reactions: Covalent bonds can be formed during chemical reactions, such as combustion reactions or synthesis reactions.
- Molecular collisions: When two molecules collide, they can share electrons and form a covalent bond.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are several types of covalent bonds, including:
- Sigma (σ) bonds: These bonds involve the sharing of electrons in a linear fashion.
- Pi (π) bonds: These bonds involve the sharing of electrons in a sideways fashion.
- Delta (δ) bonds: These bonds involve the sharing of electrons in a bent fashion.
Each type of covalent bond has its own unique characteristics and is formed through different mechanisms.

Significance of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds play a crucial role in the world of chemistry, as they are responsible for the formation of molecules. Without covalent bonds, molecules would not be able to form, and many of the substances we use every day would not exist.
Covalent bonds are also responsible for many of the properties of molecules, including their shape, polarity, and reactivity. Understanding covalent bonds is essential for understanding many of the phenomena that occur in the natural world.
Real-World Applications of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds have many real-world applications, including:
- Biochemistry: Covalent bonds are essential for the formation of biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA.
- Materials science: Covalent bonds are used to create a wide range of materials, including plastics, ceramics, and glass.
- Pharmaceuticals: Covalent bonds are used to create many pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics and painkillers.
In conclusion, covalent bonds are a fundamental aspect of chemistry, playing a crucial role in the formation of molecules. Understanding covalent bonds is essential for understanding many of the phenomena that occur in the natural world.

We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of covalent bonds and their significance in the world of chemistry. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, please leave a comment below.
What is a covalent bond?
+A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Which elements form covalent bonds?
+Covalent bonds can be formed between a wide range of elements, but they are most commonly found in molecules composed of non-metal atoms, such as carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen.
What is electronegativity?
+Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond.