The preterite tense is a fundamental aspect of Spanish grammar, and mastering it is essential for effective communication. In this article, we will delve into the world of the preterite tense, exploring its definition, uses, and conjugation.
What is the Preterite Tense?

The preterite tense, also known as the simple past tense, is a verb form used to describe completed actions that occurred in the past. It is a crucial aspect of Spanish grammar, as it allows speakers to convey events, actions, and states that have already taken place.
Uses of the Preterite Tense
The preterite tense is used to describe:
- Completed actions in the past: "Yo estudié para el examen" (I studied for the exam).
- Past habits: "Solía ir al parque todos los días" (I used to go to the park every day).
- Past states: "Ella fue una estudiante excelente" (She was an excellent student).
Conjugation of Regular Verbs in the Preterite Tense

Regular verbs in Spanish follow a specific pattern when conjugated in the preterite tense. The conjugation depends on the verb's ending (-ar, -er, or -ir).
- -ar verbs: -é, -aste, -ó, -amos, -asteis, -aron
- -er verbs: -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, -ieron
- -ir verbs: -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, -ieron
For example:
- Hablar (to speak): Yo hablé, tú hablaste, él/ella/usted habló, nosotros/as hablamos, vosotros/as habláis, ellos/as hablaron
- Comer (to eat): Yo comí, tú comiste, él/ella/usted comió, nosotros/as comimos, vosotros/as comisteis, ellos/as comieron
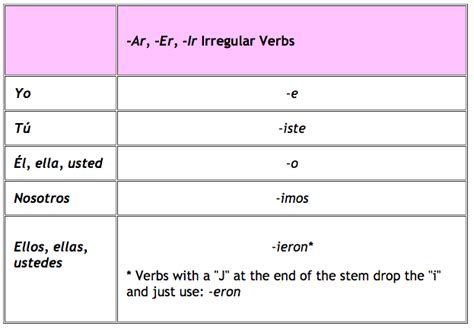
Irregular Verbs in the Preterite Tense
Irregular verbs do not follow the standard conjugation pattern. Some common irregular verbs in the preterite tense include:
- Ser (to be): Yo fui, tú fuiste, él/ella/usted fue, nosotros/as fuimos, vosotros/as fuisteis, ellos/as fueron
- Estar (to be): Yo estuve, tú estuviste, él/ella/usted estuvo, nosotros/as estuvimos, vosotros/as estuvisteis, ellos/as estuvieron
- Tener (to have): Yo tuve, tú tuviste, él/ella/usted tuvo, nosotros/as tuvimos, vosotros/as tuvisteis, ellos/as tuvieron
Using the Preterite Tense in Context

To use the preterite tense effectively, it is essential to understand the context in which it is being used. Here are some examples:
- Completed actions: "Yo terminé mi trabajo a las 5 pm" (I finished my work at 5 pm).
- Past habits: "Solía ir al gimnasio todos los días, pero ahora estoy ocupado" (I used to go to the gym every day, but now I'm busy).
- Past states: "Ella fue una excelente estudiante en la universidad" (She was an excellent student in college).
Common Mistakes When Using the Preterite Tense
When using the preterite tense, it is common to make mistakes such as:
- Using the present tense instead of the preterite tense: "Yo estudio para el examen" instead of "Yo estudié para el examen".
- Using the wrong conjugation: "Yo hablo" instead of "Yo hablé".
- Mixing up regular and irregular verb conjugations.
Practice Exercises for the Preterite Tense

To master the preterite tense, it is essential to practice conjugating verbs and using them in context. Here are some exercises:
- Conjugate the verb "hablar" in the preterite tense for all six subjects.
- Write a short paragraph using the preterite tense to describe a past event.
- Identify the correct conjugation of the verb "ser" in the preterite tense.
Conclusion: Mastering the Preterite Tense

Mastering the preterite tense is a crucial aspect of Spanish grammar. By understanding the conjugation of regular and irregular verbs, using the preterite tense in context, and practicing with exercises, you can improve your language skills and communicate effectively in Spanish.
We hope you found this article informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to share them with us. ¡Hasta luego!
What is the difference between the preterite and imperfect tenses?
+The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past, while the imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past.
How do I conjugate irregular verbs in the preterite tense?
+Irregular verbs do not follow the standard conjugation pattern. It is essential to memorize the conjugation of irregular verbs in the preterite tense.
Can I use the preterite tense to describe past habits?
+Yes, the preterite tense can be used to describe past habits, but it is more common to use the imperfect tense for this purpose.