The human body is a complex and intricate machine, comprising numerous systems that work in harmony to maintain optimal health and functionality. One of the most vital systems in the body is the musculoskeletal system, which provides structural support, protection, and mobility. Within this system, the vertebral column plays a crucial role in safeguarding one of the body's most essential organs: the spinal cord.
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or backbone, is a series of interconnected bones that extend from the base of the skull to the tailbone. It serves as a protective casing for the spinal cord, a long, thin, and delicate structure that extends from the brain to the lower back. The spinal cord is responsible for transmitting and processing nerve impulses, which enable communication between the brain and the rest of the body.

The vertebral column's protective function is multifaceted. Firstly, it provides a physical barrier against external trauma, such as impacts, compressions, or penetrations. The vertebral bones, along with the surrounding muscles and ligaments, form a robust shield that absorbs and distributes external forces, thereby safeguarding the spinal cord from injury.
Secondly, the vertebral column regulates the flow of fluids and nutrients to the spinal cord. The spinal canal, a hollow tube within the vertebral column, contains the spinal cord and provides a conduit for the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear, colorless liquid that cushions the spinal cord, removes waste products, and supplies essential nutrients.
Thirdly, the vertebral column plays a critical role in maintaining the spinal cord's optimal environment. The vertebral bones and surrounding tissues regulate the temperature, pH, and chemical composition of the spinal canal, ensuring that the spinal cord functions correctly.
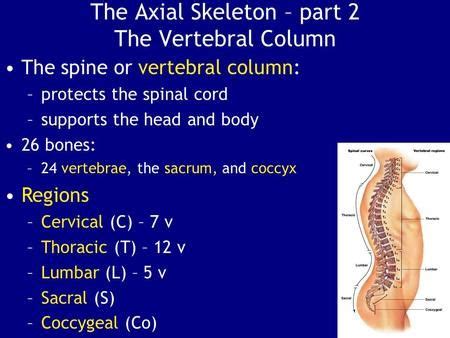
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column
The vertebral column is composed of 33 vertebrae, which are divided into five distinct regions: cervical (neck), thoracic (upper back), lumbar (lower back), sacrum (pelvis), and coccyx (tailbone). Each vertebra has a unique shape and structure, adapted to its specific function within the vertebral column.
The cervical region, comprising seven vertebrae, supports the head and enables a wide range of motion. The thoracic region, consisting of 12 vertebrae, provides attachment points for the ribs and helps to form the thoracic cage. The lumbar region, made up of five vertebrae, bears the majority of the body's weight and enables flexion, extension, and rotation.
The sacrum, a fused set of five vertebrae, forms the posterior aspect of the pelvis and provides a stable base for the vertebral column. The coccyx, a small, triangular bone, serves as the terminal end of the vertebral column and provides attachment points for muscles and ligaments.
Functions of the Vertebral Column
The vertebral column performs several critical functions, including:
- Supporting the body's weight and maintaining posture
- Facilitating movement and flexibility
- Protecting the spinal cord and surrounding nerves
- Regulating the flow of fluids and nutrients to the spinal cord
- Maintaining the optimal environment for spinal cord function

Common Disorders Affecting the Vertebral Column
Several disorders can affect the vertebral column, compromising its ability to protect the spinal cord. Some common conditions include:
- Herniated discs: The soft, gel-like center of the intervertebral disc protrudes through the outer layer, putting pressure on surrounding nerves.
- Degenerative disc disease: The intervertebral discs deteriorate, leading to reduced spinal flexibility and increased risk of herniation.
- Spinal stenosis: The spinal canal narrows, compressing the spinal cord and surrounding nerves.
- Scoliosis: The vertebral column curves abnormally, potentially compressing the spinal cord and surrounding tissues.
- Osteoporosis: The vertebral bones weaken, increasing the risk of fractures and compression.

Prevention and Treatment Strategies
While some disorders affecting the vertebral column are unavoidable, several prevention and treatment strategies can help maintain spinal health. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the vertebral column
- Engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine
- Practicing good posture to reduce strain on the vertebral column
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques and mindfulness practices
In cases where disorders have developed, treatment options may include physical therapy, pain management, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Vertebral Column
The vertebral column plays a vital role in safeguarding the spinal cord, and maintaining its health is essential for overall well-being. By understanding the structure and function of the vertebral column, as well as the common disorders that can affect it, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent spinal problems and ensure optimal spinal health.

We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the importance of the vertebral column in protecting the spinal cord. By prioritizing spinal health and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of disorders and maintain optimal overall health.
Now, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences related to spinal health. Have you or a loved one experienced a spinal disorder? What preventive measures do you take to maintain your spinal health? Share your comments below and let's start a conversation!
What is the primary function of the vertebral column?
+The primary function of the vertebral column is to protect the spinal cord and provide structural support for the body.
What are some common disorders affecting the vertebral column?
+Common disorders affecting the vertebral column include herniated discs, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, scoliosis, and osteoporosis.
How can I maintain a healthy vertebral column?
+To maintain a healthy vertebral column, it is essential to maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular exercise, practice good posture, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and manage stress.