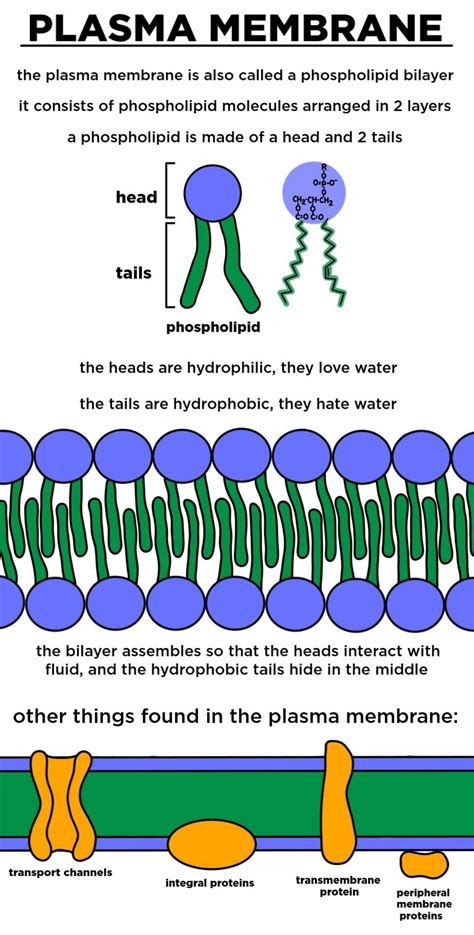
Phospholipids are a crucial component of the plasma membrane, a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that surrounds every cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out. These amphipathic molecules, with both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-fearing) regions, play a vital role in forming the plasma membrane. In this article, we will explore the five ways phospholipids form the plasma membrane and the importance of this complex structure.
Phospholipid Structure and Function

Phospholipids are composed of a phosphate group, a glycerol molecule, and two fatty acid chains. The phosphate group is hydrophilic, while the fatty acid chains are hydrophobic. This unique structure allows phospholipids to interact with both water and lipids, making them ideal for forming the plasma membrane.
Phospholipid Bilayer Formation
When phospholipids are added to water, they spontaneously form a bilayer structure. In this arrangement, the hydrophilic phosphate groups face outwards, interacting with the surrounding water, while the hydrophobic fatty acid chains face inwards, shielded from the water. This bilayer structure is the fundamental organization of the plasma membrane.
Five Ways Phospholipids Form the Plasma Membrane

Phospholipids form the plasma membrane through five key mechanisms:
1. Phospholipid Bilayer Formation
As mentioned earlier, phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer structure in water. This bilayer serves as the foundation of the plasma membrane, providing a stable and flexible structure that separates the cell from its environment.
2. Hydrogen Bonding and Electrostatic Interactions
The hydrophilic phosphate groups of phospholipids form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and other polar compounds, while the hydrophobic fatty acid chains interact through electrostatic forces. These interactions strengthen the phospholipid bilayer, making it more stable and resistant to external forces.
3. Lipid-Lipid Interactions
Phospholipids interact with each other through van der Waals forces, a type of weak intermolecular force. These interactions help to stabilize the phospholipid bilayer and regulate its fluidity.
4. Protein-Lipid Interactions
Phospholipids interact with membrane proteins, which are embedded within the bilayer or associated with its surface. These interactions play a crucial role in regulating the structure and function of the plasma membrane.
5. Cholesterol Insertion
Cholesterol molecules are inserted between phospholipid molecules, helping to regulate the fluidity of the plasma membrane. Cholesterol also interacts with phospholipids, modifying their structure and function.
Importance of the Plasma Membrane

The plasma membrane is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Its structure and function are critical for:
- Regulating the transport of ions, nutrients, and waste products
- Maintaining cellular shape and structure
- Signaling and communication with other cells
- Regulating the entry and exit of molecules
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, phospholipids play a vital role in forming the plasma membrane through their unique structure and interactions. Understanding the mechanisms of phospholipid bilayer formation and the importance of the plasma membrane is essential for appreciating the complexity of cellular biology.
As research continues to uncover the intricacies of phospholipid biology, we may uncover new opportunities for developing therapies and treatments for diseases related to plasma membrane dysfunction.
What is the main function of phospholipids in the plasma membrane?
+The main function of phospholipids in the plasma membrane is to form a stable and flexible bilayer structure that separates the cell from its environment and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
What is the role of cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
+Cholesterol molecules are inserted between phospholipid molecules, helping to regulate the fluidity of the plasma membrane and modify its structure and function.
What would happen if the plasma membrane were not present in a cell?
+If the plasma membrane were not present in a cell, the cell would not be able to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell, leading to a loss of cellular homeostasis and potentially cell death.