The concept of public goods is a fundamental idea in economics that has been extensively studied and debated by scholars and policymakers. Public goods are goods or services that are provided to everyone in a society, regardless of their ability to pay, and are often characterized by their non-rivalrous and non-excludable nature. However, there is a related concept that has gained significant attention in recent years: the idea of public goods as merit goods.
In this article, we will explore the concept of public goods, their characteristics, and the reasons why they are often considered merit goods. We will also examine the implications of this concept on public policy and the role of government in providing these goods.
What are Public Goods?
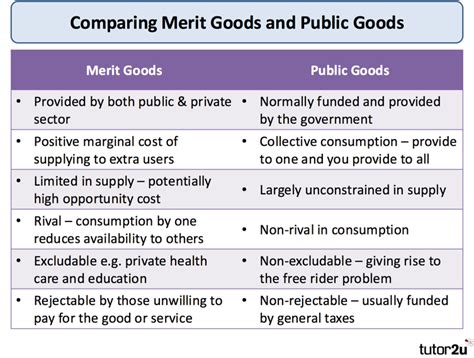
Public goods are goods or services that are provided to everyone in a society, regardless of their ability to pay. They are often characterized by two key features: non-rivalrousness and non-excludability. Non-rivalrousness means that the consumption of a public good by one individual does not reduce its availability to others. Non-excludability means that it is impossible to exclude anyone from consuming a public good, even if they have not paid for it.
Examples of public goods include national defense, public parks, and streetlights. These goods are often provided by the government, and their provision is financed through taxation.

Characteristics of Public Goods
Public goods have several key characteristics that distinguish them from private goods:
- Non-rivalrousness: The consumption of a public good by one individual does not reduce its availability to others.
- Non-excludability: It is impossible to exclude anyone from consuming a public good, even if they have not paid for it.
- Free-rider problem: Because public goods are non-excludable, individuals may not have an incentive to pay for them, as they can still consume them without paying.
- Market failure: The free-rider problem can lead to market failure, as the market may not provide an adequate supply of public goods.
What are Merit Goods?
Merit goods are goods or services that are considered to be socially desirable, but may not be provided by the market due to various reasons such as information asymmetry, externalities, or market failure. Merit goods are often characterized by their positive externalities, which means that their consumption benefits not only the individual but also others in society.
Examples of merit goods include education, healthcare, and public safety. These goods are often considered essential for the well-being of individuals and society as a whole, and their provision is often subsidized or provided by the government.

Characteristics of Merit Goods
Merit goods have several key characteristics that distinguish them from private goods:
- Positive externalities: The consumption of a merit good benefits not only the individual but also others in society.
- Social desirability: Merit goods are considered socially desirable, and their provision is often subsidized or provided by the government.
- Information asymmetry: The market may not provide an adequate supply of merit goods due to information asymmetry, as individuals may not have complete information about their benefits.
- Market failure: The market may fail to provide an adequate supply of merit goods due to externalities, information asymmetry, or other market failures.
Public Goods as Merit Goods
Public goods are often considered merit goods due to their positive externalities and social desirability. Public goods such as national defense, public parks, and streetlights provide benefits not only to the individual but also to others in society. Their provision is often subsidized or provided by the government, and their consumption is often considered essential for the well-being of individuals and society as a whole.
The concept of public goods as merit goods has significant implications for public policy. It suggests that the government should play a role in providing these goods, as the market may not provide an adequate supply due to market failure.

Implications for Public Policy
The concept of public goods as merit goods has significant implications for public policy. It suggests that the government should play a role in providing these goods, as the market may not provide an adequate supply due to market failure. The government can provide these goods through various mechanisms, such as taxation, subsidies, or provision.
The government can also use various tools to correct market failure and provide an adequate supply of public goods. These tools include regulation, taxation, and subsidies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, public goods are goods or services that are provided to everyone in a society, regardless of their ability to pay. They are often characterized by their non-rivalrous and non-excludable nature. Public goods are often considered merit goods due to their positive externalities and social desirability.
The concept of public goods as merit goods has significant implications for public policy. It suggests that the government should play a role in providing these goods, as the market may not provide an adequate supply due to market failure. The government can provide these goods through various mechanisms, such as taxation, subsidies, or provision.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive understanding of the concept of public goods as merit goods. We encourage you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic.
What are public goods?
+Public goods are goods or services that are provided to everyone in a society, regardless of their ability to pay.
What are merit goods?
+Merit goods are goods or services that are considered to be socially desirable, but may not be provided by the market due to various reasons such as information asymmetry, externalities, or market failure.
Why are public goods considered merit goods?
+Public goods are often considered merit goods due to their positive externalities and social desirability.