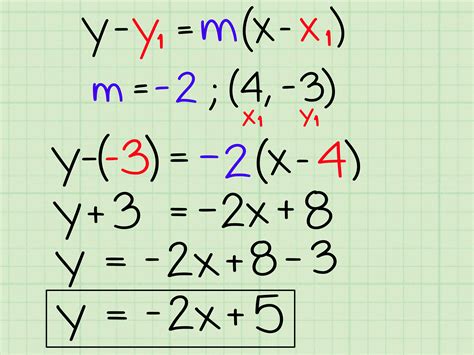Are you struggling to understand the slope-intercept form in math? Do you want to master this concept in a few easy steps? Look no further! In this article, we will break down the slope-intercept form into simple, manageable steps that will help you grasp this concept in no time.
Mathway slope-intercept form is a fundamental concept in algebra, used to graph linear equations and solve problems involving lines and slopes. However, for many students, this concept can be overwhelming, especially when dealing with variables and coefficients. But don't worry, with our 5-step guide, you'll be a pro in no time!
What is Slope-Intercept Form?

Before we dive into our 5-step guide, let's quickly review what slope-intercept form is. Slope-intercept form is a way of writing linear equations in the form y = mx + b, where:
- m is the slope of the line
- b is the y-intercept (the point where the line intersects the y-axis)
This form is useful for graphing lines and solving problems involving linear equations.
Step 1: Understand the Slope
The slope of a line is a measure of how steep it is. It can be positive, negative, or zero. To calculate the slope, you need to know two points on the line. The formula for slope is:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are two points on the line.
Step 2: Find the Y-Intercept

The y-intercept is the point where the line intersects the y-axis. To find the y-intercept, you can use the slope-intercept form of the equation: y = mx + b. Since the y-intercept is the point where x = 0, you can substitute x = 0 into the equation and solve for y.
b = y-intercept
Step 3: Write the Equation in Slope-Intercept Form
Now that you have the slope and y-intercept, you can write the equation in slope-intercept form: y = mx + b. Make sure to plug in the values of m and b correctly.
y = mx + b
Step 4: Graph the Line

To graph the line, start by plotting the y-intercept (0, b) on the y-axis. Then, use the slope to find another point on the line. Since the slope is the change in y divided by the change in x, you can move up or down the y-axis by the slope value, and then move left or right on the x-axis by 1 unit.
Repeat this process several times to create a series of points on the line. Finally, connect the points to form a straight line.
Step 5: Practice, Practice, Practice!
The final step is to practice, practice, practice! The more you practice writing equations in slope-intercept form and graphing lines, the more comfortable you'll become with this concept.
Try working on some sample problems, such as:
- Write the equation of the line with slope 2 and y-intercept 3.
- Graph the line with equation y = -2x + 4.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When working with slope-intercept form, here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Confusing the slope and y-intercept
- Plugging in incorrect values for m and b
- Forgetting to graph the y-intercept
- Not labeling the axes correctly
Real-World Applications of Slope-Intercept Form

Slope-intercept form has many real-world applications, including:
- Physics: slope-intercept form is used to describe the motion of objects
- Engineering: slope-intercept form is used to design roads and bridges
- Economics: slope-intercept form is used to model supply and demand curves
In conclusion, mastering the slope-intercept form takes practice, but with our 5-step guide, you'll be well on your way to becoming a pro! Remember to understand the slope, find the y-intercept, write the equation in slope-intercept form, graph the line, and practice, practice, practice!
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
+The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
How do I find the y-intercept of a line?
+To find the y-intercept, substitute x = 0 into the equation and solve for y.
What is the difference between the slope and y-intercept?
+The slope is the change in y divided by the change in x, while the y-intercept is the point where the line intersects the y-axis.