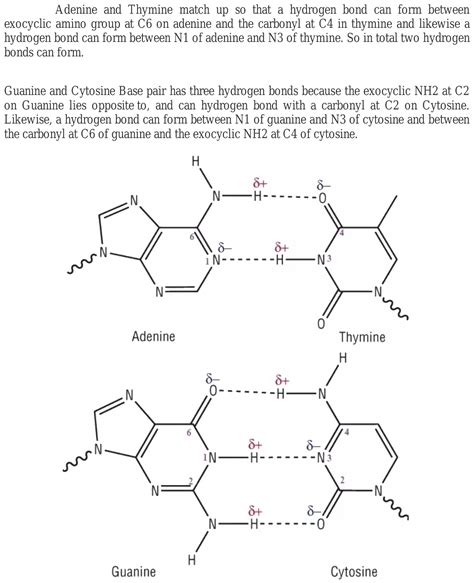
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of DNA, and the bonding between adenine and thymine is a perfect example of this. The adenine-thymine (A-T) base pair is one of the two types of base pairs that make up the DNA molecule, the other being the guanine-cytosine (G-C) base pair. In this article, we will delve into the world of hydrogen bonds and explore the intricacies of the adenine-thymine bond.

What are Hydrogen Bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are a type of weak chemical bond that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of molecules, particularly in biological systems. They are formed when a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, is attracted to another electronegative atom. This attraction is due to the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and the partial negative charge on the electronegative atom.
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for the structure and properties of many biomolecules, including DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates. They are also involved in many biological processes, such as protein folding, enzyme-substrate interactions, and DNA replication.
Adenine and Thymine: A Brief Overview
Adenine and thymine are two of the four nucleotide bases that make up the DNA molecule. Adenine is a purine base, while thymine is a pyrimidine base. These two bases are complementary to each other, meaning that they have a specific shape and chemical structure that allows them to pair with each other.
Adenine has a double ring structure, with a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring. Thymine, on the other hand, has a single six-membered ring. The structure of adenine and thymine allows them to form a specific arrangement of hydrogen bonds, which is essential for the stability of the DNA molecule.
The Adenine-Thymine Hydrogen Bond
The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is a specific type of hydrogen bond that forms between the adenine and thymine bases. This bond is responsible for the pairing of adenine and thymine in the DNA molecule.
The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is formed between the N1 atom of adenine and the N3 atom of thymine. This bond is stabilized by the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom bonded to the N1 atom of adenine and the partial negative charge on the N3 atom of thymine.

Properties of the Adenine-Thymine Hydrogen Bond
The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond has several properties that are essential for its function in the DNA molecule. Some of these properties include:
- Strength: The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is a relatively weak bond, with a bond energy of around 3 kcal/mol. This weakness allows the bond to be easily broken and reformed, which is essential for the replication and transcription of DNA.
- Specificity: The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is highly specific, meaning that it can only form between adenine and thymine bases. This specificity is due to the unique shape and chemical structure of the two bases.
- Stability: The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is relatively stable, meaning that it can withstand the thermal fluctuations and chemical reactions that occur in the cell.
Role of the Adenine-Thymine Hydrogen Bond in DNA Structure and Function
The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond plays a crucial role in the structure and function of the DNA molecule. Some of the key roles of this bond include:
- DNA replication: The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is essential for the replication of DNA, as it allows the template strand to be copied accurately.
- DNA transcription: The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is also involved in the transcription of DNA, as it helps to stabilize the RNA-DNA complex.
- DNA stability: The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond helps to maintain the stability of the DNA molecule by providing a specific arrangement of hydrogen bonds that holds the two strands together.

Conclusion: The Adenine-Thymine Hydrogen Bond: A Vital Component of DNA
In conclusion, the adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is a vital component of the DNA molecule, playing a crucial role in its structure and function. This bond is responsible for the pairing of adenine and thymine bases, which is essential for the replication and transcription of DNA. The unique properties of the adenine-thymine hydrogen bond, including its strength, specificity, and stability, make it an essential component of the DNA molecule.
We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the adenine-thymine hydrogen bond and its role in the DNA molecule. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
What is the adenine-thymine hydrogen bond?
+The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is a specific type of hydrogen bond that forms between the adenine and thymine bases in the DNA molecule.
What is the role of the adenine-thymine hydrogen bond in DNA replication?
+The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond is essential for the replication of DNA, as it allows the template strand to be copied accurately.
What is the strength of the adenine-thymine hydrogen bond?
+The adenine-thymine hydrogen bond has a bond energy of around 3 kcal/mol, making it a relatively weak bond.