Bromine is a fascinating element that plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and processes. Its unique properties make it an essential component in many industries, from pharmaceuticals to water treatment. One of the key aspects of bromine is its bonding capacity, which is the focus of this article. We will delve into the world of bromine bonding, exploring how many bonds it can form and the factors that influence its bonding behavior.
Bromine is a halogen, a group of elements that are known for their reactivity and ability to form bonds with other elements. In its elemental form, bromine is a reddish-brown liquid that readily vaporizes to form a toxic gas. Its atomic number is 35, and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5. This configuration indicates that bromine has seven valence electrons, which are the electrons involved in bonding.
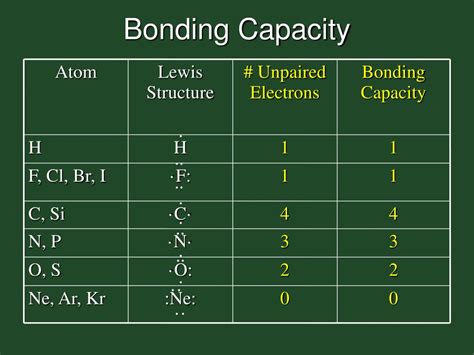
How Many Bonds Can Bromine Form?

Bromine can form one, three, or five bonds, depending on the specific reaction and the other elements involved. This variability in bonding capacity is due to the different ways in which bromine can share its valence electrons.
- One bond: In some reactions, bromine can form a single bond by sharing one pair of electrons with another element. This typically occurs when bromine reacts with a highly electronegative element, such as oxygen or fluorine.
- Three bonds: Bromine can also form three bonds by sharing three pairs of electrons with other elements. This is often seen in reactions involving bromine and elements like nitrogen or phosphorus.
- Five bonds: In some cases, bromine can form five bonds by sharing five pairs of electrons with other elements. This is less common but can occur in reactions involving bromine and highly reactive elements like sodium or potassium.
Factors Influencing Bromine Bonding Capacity
Several factors can influence the bonding capacity of bromine, including:
- Electronegativity: The electronegativity of the other element involved in the reaction can affect the bonding capacity of bromine. Highly electronegative elements tend to form single bonds with bromine, while less electronegative elements can form multiple bonds.
- Atomic size: The size of the other element can also impact the bonding capacity of bromine. Larger elements tend to form multiple bonds with bromine, while smaller elements form single bonds.
- Reaction conditions: The conditions under which the reaction occurs can also influence the bonding capacity of bromine. For example, high temperatures or pressures can favor the formation of multiple bonds.
Bromine Bonding Mechanisms

Bromine bonding mechanisms can be classified into several types, including:
- Covalent bonding: This type of bonding involves the sharing of electrons between bromine and another element.
- Ionic bonding: This type of bonding involves the transfer of electrons between bromine and another element, resulting in the formation of ions.
- Dative bonding: This type of bonding involves the donation of electrons from bromine to another element.
Examples of Bromine Bonding
Some examples of bromine bonding include:
- Bromine and oxygen: Bromine can form a single bond with oxygen to form bromine oxide (Br2O).
- Bromine and nitrogen: Bromine can form three bonds with nitrogen to form bromine nitride (Br3N).
- Bromine and sodium: Bromine can form five bonds with sodium to form sodium bromide (NaBr).
Applications of Bromine Bonding

The bonding capacity of bromine has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Bromine is used as a precursor to synthesize various pharmaceuticals, such as sedatives and anticonvulsants.
- Water treatment: Bromine is used as a disinfectant in water treatment plants to kill bacteria and other microorganisms.
- Pesticides: Bromine is used as an active ingredient in pesticides to control pests and diseases in crops.
In conclusion, the bonding capacity of bromine is a complex and multifaceted topic that plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and processes. By understanding how many bonds bromine can form and the factors that influence its bonding behavior, we can better appreciate the importance of this element in various industries.
What is the atomic number of bromine?
+The atomic number of bromine is 35.
How many bonds can bromine form?
+Bromine can form one, three, or five bonds, depending on the specific reaction and the other elements involved.
What are some examples of bromine bonding?
+Some examples of bromine bonding include bromine and oxygen, bromine and nitrogen, and bromine and sodium.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of bromine bonding capacity. If you have any further questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.