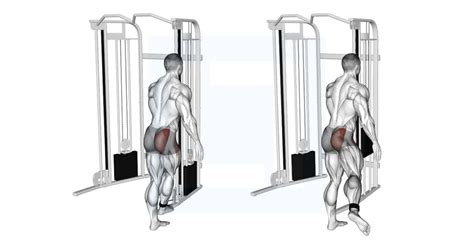
As one of the most critical muscles in the human body, the glutes play a vital role in maintaining good posture, facilitating movement, and providing stability to the hips and lower back. Among the three gluteal muscles, the gluteus medius is often overlooked, yet it is essential for hip abduction, rotation, and stabilization. One effective exercise to target the gluteus medius is the gluteus medius kickback, a variation of the traditional donkey kick. In this article, we will explore the importance of mastering the gluteus medius kickback form for stronger glutes.

The gluteus medius kickback is an isolation exercise that specifically targets the gluteus medius muscle, helping to improve hip stability, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance overall athletic performance. However, to reap the benefits of this exercise, it is crucial to master the proper form and technique. In this article, we will delve into the world of gluteus medius kickbacks, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps involved in performing this exercise correctly.
Understanding the Gluteus Medius Muscle
The gluteus medius muscle is a fan-shaped muscle located on the outer aspect of the hip, originating from the ilium and inserting into the greater trochanter of the femur. This muscle is responsible for hip abduction, rotation, and stabilization, playing a vital role in maintaining balance and facilitating movement.

The gluteus medius muscle is divided into two parts: the anterior fibers, which assist in hip flexion and internal rotation, and the posterior fibers, which help with hip extension and external rotation. Weak or underactive gluteus medius muscles can lead to poor hip stability, resulting in injuries such as hip strains, lower back pain, and knee problems.
Benefits of the Gluteus Medius Kickback
The gluteus medius kickback offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved hip stability: Strengthening the gluteus medius muscle helps to enhance hip stability, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall athletic performance.
- Increased strength: The gluteus medius kickback helps to build strength in the glutes, hips, and lower back, making everyday activities easier and reducing the risk of injury.
- Better posture: Strengthening the gluteus medius muscle can help improve posture by pulling the pelvis into a more neutral position.
- Enhanced athletic performance: The gluteus medius kickback can help improve athletic performance by increasing power, speed, and agility.
Step-by-Step Guide to Mastering the Gluteus Medius Kickback Form
To perform the gluteus medius kickback correctly, follow these steps:
- Start in a tabletop position: Begin on your hands and knees, with your hands shoulder-width apart and your knees directly under your hips.
- Lift one leg: Lift one leg out to the side, keeping your knee bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Kick back: Slowly kick your leg back, keeping your foot flexed and your knee straight.
- Hold and squeeze: Hold for a brief moment, squeezing your glutes and hips.
- Return to the starting position: Slowly return to the starting position, repeating on the other side.

Tips and Variations
- Use a resistance band: Adding a resistance band can increase the intensity of the exercise and help target the gluteus medius muscle more effectively.
- Lift your leg higher: Lifting your leg higher can increase the range of motion and challenge the gluteus medius muscle more.
- Focus on slow and controlled movements: Slow and controlled movements can help ensure that you are targeting the correct muscle and avoiding injury.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When performing the gluteus medius kickback, it is essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to injury or ineffective training. Some common mistakes include:
- Letting the knee extend: Allowing the knee to extend can put unnecessary strain on the joint and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Not squeezing the glutes: Failing to squeeze the glutes can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and lead to poor form.
- Using momentum: Using momentum can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and increase the risk of injury.

Conclusion
Mastering the gluteus medius kickback form is essential for stronger glutes, improved hip stability, and enhanced athletic performance. By following the steps outlined in this article and avoiding common mistakes, you can effectively target the gluteus medius muscle and reap the benefits of this exercise. Remember to focus on slow and controlled movements, use a resistance band if necessary, and squeeze your glutes to ensure that you are getting the most out of this exercise.

Call to Action
We hope that this article has helped you understand the importance of mastering the gluteus medius kickback form. If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below. Share this article with your friends and family to help them achieve stronger glutes and improved hip stability.
What is the gluteus medius muscle?
+The gluteus medius muscle is a fan-shaped muscle located on the outer aspect of the hip, originating from the ilium and inserting into the greater trochanter of the femur.
What are the benefits of the gluteus medius kickback?
+The gluteus medius kickback offers numerous benefits, including improved hip stability, increased strength, better posture, and enhanced athletic performance.
How do I perform the gluteus medius kickback correctly?
+To perform the gluteus medius kickback correctly, follow these steps: start in a tabletop position, lift one leg, kick back, hold and squeeze, and return to the starting position.