When it comes to the world of taxes, it's easy to get lost in the sea of forms and regulations. Two forms that are often confused with one another are Form 8834 and Form 8936. While they may seem similar, they serve distinct purposes and have different requirements. In this article, we'll delve into the key differences between Form 8834 and Form 8936, so you can better understand which form is right for your needs.
Understanding Form 8834
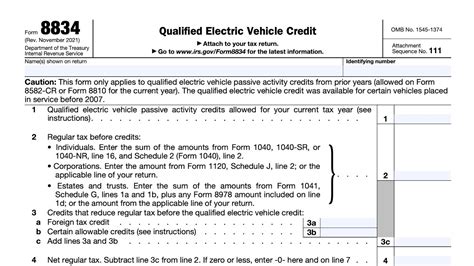
Form 8834, also known as the Qualified Electric Vehicle Credit, is a tax form used to claim a credit for the purchase of a qualified electric vehicle. This form is designed for individuals and businesses that have purchased an electric vehicle and want to take advantage of the tax credit available under Section 30 of the Internal Revenue Code.
The credit is calculated based on the vehicle's battery capacity, with a maximum credit of $7,500 available. To qualify, the vehicle must have a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours and be propelled by an electric motor. The credit is phased out once the manufacturer sells 200,000 qualifying vehicles.

Understanding Form 8936
Form 8936, also known as the Qualified Plug-in Electric Drive Motor Vehicle Credit, is another tax form used to claim a credit for the purchase of a qualified plug-in electric drive motor vehicle. This form is also designed for individuals and businesses that have purchased a qualifying vehicle and want to take advantage of the tax credit available under Section 30D of the Internal Revenue Code.
The credit is calculated based on the vehicle's battery capacity, with a maximum credit of $7,500 available. To qualify, the vehicle must have a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours and be propelled by an electric motor. The credit is phased out once the manufacturer sells 200,000 qualifying vehicles.

Key Differences Between Form 8834 and Form 8936
While both forms are used to claim a credit for the purchase of an electric vehicle, there are key differences between Form 8834 and Form 8936.
Vehicle Requirements
One of the main differences between the two forms is the type of vehicle that qualifies for the credit. Form 8834 requires the vehicle to have a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours and be propelled by an electric motor. Form 8936, on the other hand, requires the vehicle to have a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours and be propelled by an electric motor, but also requires the vehicle to be a plug-in electric drive motor vehicle.
Battery Capacity
Another key difference is the battery capacity required to qualify for the credit. Form 8834 requires a minimum battery capacity of 4 kilowatt-hours, while Form 8936 requires a minimum battery capacity of 4 kilowatt-hours, but also requires the vehicle to have a battery capacity of at least 2.5 kilowatt-hours per 500 pounds of vehicle weight.
Credit Calculation
The credit calculation is also different between the two forms. Form 8834 calculates the credit based on the vehicle's battery capacity, with a maximum credit of $7,500 available. Form 8936 also calculates the credit based on the vehicle's battery capacity, but also takes into account the vehicle's weight and battery capacity per weight.

Which Form is Right for You?
Now that we've explained the key differences between Form 8834 and Form 8936, you may be wondering which form is right for you. If you've purchased an electric vehicle and want to take advantage of the tax credit available, you'll need to determine which form is required.
If you've purchased a qualified electric vehicle with a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours, you'll likely need to file Form 8834. If you've purchased a plug-in electric drive motor vehicle with a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours and a battery capacity of at least 2.5 kilowatt-hours per 500 pounds of vehicle weight, you'll likely need to file Form 8936.
Consult a Tax Professional
To ensure you're filing the correct form and taking advantage of the tax credit available, it's always best to consult a tax professional. They can help you determine which form is required and ensure you're meeting all the necessary requirements.

Conclusion
In conclusion, while Form 8834 and Form 8936 may seem similar, they serve distinct purposes and have different requirements. By understanding the key differences between the two forms, you can ensure you're filing the correct form and taking advantage of the tax credit available. Remember to consult a tax professional to ensure you're meeting all the necessary requirements.
Take Action Today
Don't miss out on the opportunity to take advantage of the tax credit available for purchasing an electric vehicle. Take action today and consult a tax professional to determine which form is right for you.

FAQ Section:
What is the difference between Form 8834 and Form 8936?
+Form 8834 is used to claim a credit for the purchase of a qualified electric vehicle, while Form 8936 is used to claim a credit for the purchase of a plug-in electric drive motor vehicle.
Which form do I need to file if I've purchased an electric vehicle?
+If you've purchased a qualified electric vehicle with a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours, you'll likely need to file Form 8834. If you've purchased a plug-in electric drive motor vehicle with a battery capacity of at least 4 kilowatt-hours and a battery capacity of at least 2.5 kilowatt-hours per 500 pounds of vehicle weight, you'll likely need to file Form 8936.
Can I file both Form 8834 and Form 8936?
+No, you can only file one form. If you're eligible for both forms, you'll need to determine which form is required based on the type of vehicle you've purchased.