The building blocks of life, amino acids, are the foundation upon which all proteins are constructed. The human body relies on these proteins to perform a multitude of functions, from regulating metabolism to constructing tissues. But have you ever wondered how these amino acids come together to form proteins? In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of protein synthesis and explore the 5 ways amino acids join to form proteins.
The Importance of Protein Synthesis

Protein synthesis is a complex process that involves the assembly of amino acids into proteins. This process is essential for the growth, maintenance, and repair of tissues in the body. Without protein synthesis, the body would be unable to produce the necessary proteins to perform vital functions, leading to a range of health problems.
What Are Amino Acids?

Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both a carboxyl (-COOH) and an amino (-NH2) group. These groups are attached to a central carbon atom, which is also bonded to a hydrogen atom and a side chain (R-group). There are 20 different amino acids that the human body uses to build proteins, each with its unique side chain.
The 5 Ways Amino Acids Join to Form Proteins
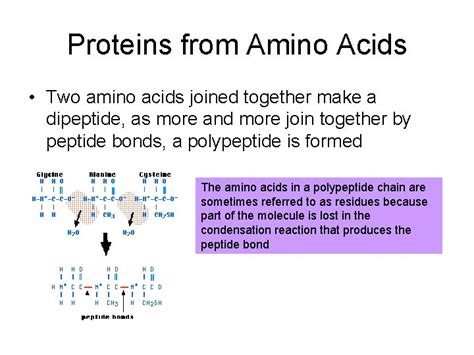
1. Peptide Bond Formation

The first way amino acids join to form proteins is through the formation of peptide bonds. This process involves the condensation of two amino acids, resulting in the loss of a water molecule and the formation of a peptide bond. This bond is a covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another.
2. Hydrogen Bonding

The second way amino acids join to form proteins is through hydrogen bonding. This type of bonding occurs between the positively charged amino group and the negatively charged carboxyl group of adjacent amino acids. Hydrogen bonds are weak bonds that help to stabilize the structure of proteins.
3. Disulfide Bridge Formation

The third way amino acids join to form proteins is through the formation of disulfide bridges. This process involves the oxidation of two cysteine amino acids, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond between the sulfur atoms. Disulfide bridges help to stabilize the structure of proteins and are commonly found in proteins that are secreted from cells.
4. Ionic Interactions

The fourth way amino acids join to form proteins is through ionic interactions. This type of interaction occurs between positively charged amino acids (such as arginine and lysine) and negatively charged amino acids (such as glutamate and aspartate). Ionic interactions help to stabilize the structure of proteins and are commonly found in proteins that are involved in binding to other molecules.
5. Van der Waals Forces

The fifth way amino acids join to form proteins is through van der Waals forces. This type of interaction occurs between non-polar amino acids (such as alanine and valine) and is a result of the attractive and repulsive forces between molecules. Van der Waals forces help to stabilize the structure of proteins and are commonly found in proteins that are involved in binding to other molecules.
Conclusion: The Complexity of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is a complex process that involves the assembly of amino acids into proteins. The 5 ways amino acids join to form proteins, including peptide bond formation, hydrogen bonding, disulfide bridge formation, ionic interactions, and van der Waals forces, all play a crucial role in the formation of proteins. Understanding these processes is essential for appreciating the complexity of protein synthesis and the importance of proteins in the human body.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of how amino acids join to form proteins. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to comment below.
What is protein synthesis?
+Protein synthesis is the process by which cells build proteins from amino acids.
What are the 20 amino acids used by the human body to build proteins?
+The 20 amino acids used by the human body to build proteins are: alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, serine, threonine, tryptophan, tyrosine, and valine.
What is the difference between a peptide bond and a disulfide bridge?
+A peptide bond is a covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another. A disulfide bridge is a covalent bond between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine amino acids.