Metals are a group of elements known for their ability to lose electrons to form ions with a positive charge. This process is called ionization, and it's a fundamental concept in chemistry. But do metals always form positive ions? Let's dive deeper to find out.
Metals are typically found on the left side and center of the periodic table, and they tend to lose electrons to form cations, which are positively charged ions. This is because metals have a relatively low number of electrons in their outermost energy level, making it easy for them to lose them and form a positive ion.
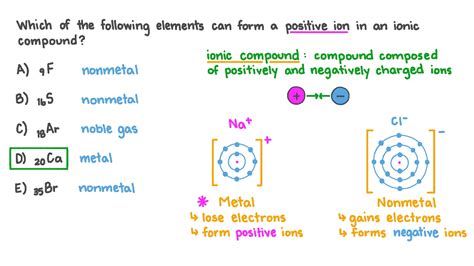
For example, when sodium (Na) loses an electron, it forms a positively charged ion, Na+. This process is represented by the equation:
Na → Na+ + e-
Similarly, when calcium (Ca) loses two electrons, it forms a positively charged ion, Ca2+. This process is represented by the equation:
Ca → Ca2+ + 2e-
In both cases, the metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positive ion. This is a common characteristic of metals, and it's why they tend to form positive ions.
However, it's worth noting that some metals can also form negative ions, although this is less common. When a metal forms a negative ion, it's called an anion. This typically occurs when a metal reacts with a nonmetal, such as oxygen or chlorine, to form a compound.
For example, when potassium (K) reacts with oxygen (O), it forms a compound called potassium oxide (K2O). In this compound, the potassium atoms lose electrons to form positive ions, while the oxygen atoms gain electrons to form negative ions. This process is represented by the equation:
4K + O2 → 2K2O
In this case, the potassium ions have a positive charge (K+), while the oxide ions have a negative charge (O2-).

Another example is when a metal like sodium reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride (NaCl). In this compound, the sodium atoms lose electrons to form positive ions, while the chlorine atoms gain electrons to form negative ions. This process is represented by the equation:
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
In this case, the sodium ions have a positive charge (Na+), while the chloride ions have a negative charge (Cl-).
In summary, metals tend to form positive ions by losing electrons, but they can also form negative ions in certain circumstances, such as when reacting with nonmetals.
Why Do Metals Form Positive Ions?
So, why do metals tend to form positive ions? There are several reasons for this:
- Low Ionization Energy: Metals have a relatively low ionization energy, which is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. This makes it easy for metals to lose electrons and form positive ions.
- High Electronegativity: Metals tend to have a low electronegativity, which is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. This means that metals are less likely to attract electrons and more likely to lose them, forming positive ions.
- Large Atomic Radius: Metals tend to have a large atomic radius, which means that their electrons are farther away from the nucleus. This makes it easier for metals to lose electrons and form positive ions.
These factors combined make it more likely for metals to form positive ions than negative ions.
What Are the Properties of Metal Ions?
Metal ions have several properties that are worth noting:
- Charge: Metal ions have a positive charge, ranging from +1 to +3 or more.
- Size: Metal ions are typically smaller than the corresponding neutral atom.
- Electronegativity: Metal ions have a high electronegativity, which means they tend to attract electrons.
- Reactivity: Metal ions can be highly reactive, especially when they have a high charge.
These properties make metal ions important in many chemical reactions and biological processes.
Examples of Metal Ions
Here are some examples of metal ions:
- Sodium ion (Na+)
- Calcium ion (Ca2+)
- Potassium ion (K+)
- Magnesium ion (Mg2+)
- Aluminum ion (Al3+)
These metal ions are commonly found in many biological systems, such as the human body, and play important roles in many chemical reactions.

In conclusion, metals tend to form positive ions by losing electrons, although they can also form negative ions in certain circumstances. The properties of metal ions, such as their charge, size, electronegativity, and reactivity, make them important in many chemical reactions and biological processes.
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about metal ions, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others.
Real-World Applications of Metal Ions
Metal ions have many real-world applications, including:
- Biological Systems: Metal ions play important roles in many biological systems, such as the human body, where they help regulate various physiological processes.
- Chemical Reactions: Metal ions are used as catalysts in many chemical reactions, helping to speed up the reaction rate and improve efficiency.
- Materials Science: Metal ions are used in the production of many materials, such as alloys, ceramics, and glass.
- Environmental Science: Metal ions are used to clean up pollutants in the environment, such as heavy metals in contaminated soil.
These are just a few examples of the many real-world applications of metal ions.

In summary, metal ions have many important properties and applications, and understanding them is crucial in many fields of science and engineering.
Common Misconceptions About Metal Ions
Here are some common misconceptions about metal ions:
- All Metals Form Positive Ions: While most metals form positive ions, some can also form negative ions in certain circumstances.
- Metal Ions Are Always Highly Reactive: While some metal ions are highly reactive, others are relatively stable and less reactive.
- Metal Ions Are Only Found in Inorganic Compounds: Metal ions can be found in both inorganic and organic compounds.
It's essential to understand the correct properties and behavior of metal ions to avoid these common misconceptions.

In conclusion, metal ions have many important properties and applications, and understanding them is crucial in many fields of science and engineering. By avoiding common misconceptions and understanding the correct behavior of metal ions, we can better appreciate their importance in many biological and chemical processes.
Conclusion
In this article, we've explored the properties and behavior of metal ions, including their tendency to form positive ions, their properties, and their applications. We've also discussed common misconceptions about metal ions and how to avoid them.
We hope you've found this article informative and helpful in understanding the fascinating world of metal ions. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others.
Share Your Thoughts
We'd love to hear your thoughts on metal ions! Please comment below and share your questions, insights, or experiences with metal ions.
FAQ Section
What is a metal ion?
+A metal ion is a positively charged ion formed by a metal atom that has lost one or more electrons.
Why do metals tend to form positive ions?
+Metals tend to form positive ions because they have a relatively low ionization energy, high electronegativity, and large atomic radius.
What are some examples of metal ions?
+Some examples of metal ions include sodium ion (Na+), calcium ion (Ca2+), potassium ion (K+), magnesium ion (Mg2+), and aluminum ion (Al3+).