Metals play a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, from the devices we use to the cars we drive. But have you ever wondered how metals form cations, which are positively charged ions? In this article, we will delve into the world of metal cations and explore the five ways they form.

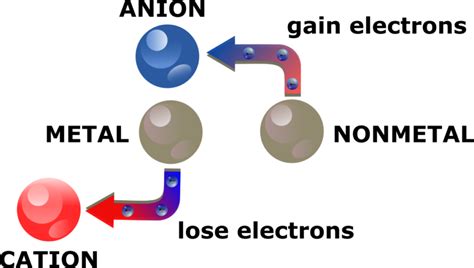
Metals are known for their ability to lose electrons, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions, or cations. This process is crucial in various chemical reactions, including those that occur in our bodies. But how do metals form cations? Let's take a closer look.
What are Cations?
Before we dive into the ways metals form cations, it's essential to understand what cations are. Cations are positively charged ions that are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. This process is known as ionization. Cations are typically formed by metals, which are known for their ability to lose electrons.
Characteristics of Cations
Cations have several characteristics that distinguish them from anions, which are negatively charged ions. Some of the key characteristics of cations include:
- Positive charge: Cations have a positive charge due to the loss of electrons.
- Small size: Cations are typically smaller than anions due to the loss of electrons.
- High charge density: Cations have a high charge density, which means they have a high charge-to-size ratio.
5 Ways Metals Form Cations
Now that we have a basic understanding of cations, let's explore the five ways metals form cations.
1. Ionization
Ionization is the process by which an atom loses one or more electrons to form a cation. This process occurs when a metal atom is heated or subjected to high energy levels. The energy required to remove an electron from a metal atom is known as the ionization energy.

For example, when a sodium atom is heated, it loses an electron to form a positively charged sodium ion.
Na → Na+ + e-
2. Oxidation
Oxidation is the process by which an atom loses one or more electrons to form a cation. This process occurs when a metal atom reacts with an oxidizing agent, such as oxygen. The oxidizing agent removes electrons from the metal atom, resulting in the formation of a cation.

For example, when iron reacts with oxygen, it forms a positively charged iron ion.
Fe + O2 → Fe2+ + O2-
3. Electrolysis
Electrolysis is the process by which an electric current is used to drive a chemical reaction. In the case of metal cations, electrolysis can be used to remove electrons from a metal atom, resulting in the formation of a cation.

For example, when a sodium chloride solution is subjected to electrolysis, the sodium ions are reduced to form a positively charged sodium ion.
NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
4. Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of electrons between an acid and a base. In some cases, acid-base reactions can result in the formation of metal cations.

For example, when hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, the sodium ion is formed.
HCl + NaOH → Na+ + Cl- + H2O
5. Complexation
Complexation is the process by which a metal ion forms a complex with a ligand. In some cases, complexation can result in the formation of a metal cation.

For example, when copper reacts with ammonia, it forms a positively charged copper complex.
Cu + 4NH3 → [Cu(NH3)4]2+
As we have seen, metals can form cations in a variety of ways, including ionization, oxidation, electrolysis, acid-base reactions, and complexation. Understanding these processes is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
What is a cation?
+A cation is a positively charged ion that is formed when an atom loses one or more electrons.
What is ionization?
+Ionization is the process by which an atom loses one or more electrons to form a cation.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
+A cation is a positively charged ion, while an anion is a negatively charged ion.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of how metals form cations. Whether you're a student or a professional, understanding the basics of chemistry is crucial in various fields. We encourage you to share this article with your friends and colleagues and to ask any questions you may have in the comments section below.