As we delve into the world of biochemistry, it's hard to ignore the significance of glucose, a simple sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for our bodies. Glucose is a versatile molecule that can exist in multiple forms, one of which is its cyclic form. In this article, we'll explore the cyclic form of glucose, its structure, benefits, and importance in biological processes.
The Cyclic Form of Glucose: A Structural Overview

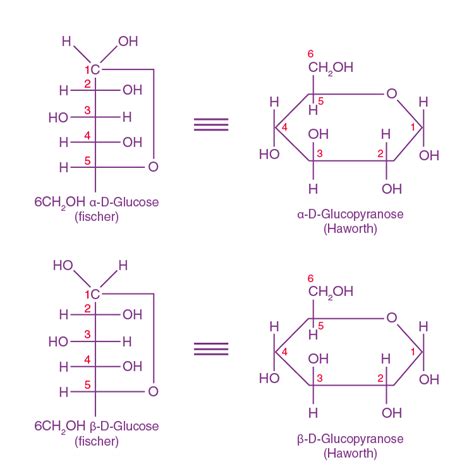
Glucose is a hexose sugar, meaning it contains six carbon atoms. In its cyclic form, glucose assumes a ring-like structure, also known as a hemiacetal. This structure is formed when the hydroxyl group (-OH) on the fifth carbon atom reacts with the aldehyde group (-CHO) on the first carbon atom, resulting in a stable ring. The cyclic form of glucose is also known as glucopyranose.
Types of Cyclic Glucose
There are two main types of cyclic glucose: alpha-glucose and beta-glucose. The difference between these two forms lies in the orientation of the hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon atom (the carbon atom that is part of the aldehyde group). In alpha-glucose, the hydroxyl group is oriented below the ring, while in beta-glucose, it is oriented above the ring.
The Benefits of Cyclic Glucose

The cyclic form of glucose has several benefits that make it an essential molecule in biological processes. Some of these benefits include:
- Increased stability: The ring structure of cyclic glucose makes it more stable than its linear counterpart, allowing it to withstand various chemical and physical conditions.
- Improved solubility: The cyclic form of glucose is more soluble in water than its linear form, making it easier to transport and metabolize in the body.
- Enhanced biological activity: The cyclic form of glucose is more readily recognized and utilized by enzymes and other biological molecules, making it a more effective energy source.
Biological Processes Involving Cyclic Glucose
Cyclic glucose plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Glycolysis: The breakdown of glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP.
- Gluconeogenesis: The synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as amino acids and lactate.
- Glycogen synthesis: The storage of glucose in the form of glycogen, a complex carbohydrate.
The Role of Cyclic Glucose in Energy Production

Cyclic glucose is the primary energy source for our bodies. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which is then converted into cyclic glucose. This cyclic form of glucose is then transported to cells, where it is converted into energy in the form of ATP through the process of glycolysis.
The Importance of Cyclic Glucose in Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells lack mitochondria, the organelles responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration. As a result, red blood cells rely heavily on cyclic glucose as an energy source. The cyclic form of glucose is converted into ATP through glycolysis, providing the energy needed to maintain the structural integrity of red blood cells.
Conclusion: The Significance of Cyclic Glucose

In conclusion, the cyclic form of glucose is a vital molecule that plays a central role in biological processes. Its unique structure and benefits make it an essential energy source for our bodies. Understanding the importance of cyclic glucose can help us appreciate the complexities of biochemistry and the importance of this molecule in maintaining life.
Now, we'd love to hear from you! Do you have any questions about cyclic glucose or its role in biological processes? Share your thoughts in the comments section below. Don't forget to share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the significance of cyclic glucose.
What is the difference between alpha-glucose and beta-glucose?
+The main difference between alpha-glucose and beta-glucose lies in the orientation of the hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon atom. In alpha-glucose, the hydroxyl group is oriented below the ring, while in beta-glucose, it is oriented above the ring.
What is the role of cyclic glucose in energy production?
+Cyclic glucose is the primary energy source for our bodies. It is converted into energy in the form of ATP through the process of glycolysis.
Why is cyclic glucose important in red blood cells?
+Red blood cells lack mitochondria, the organelles responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration. As a result, red blood cells rely heavily on cyclic glucose as an energy source.