In the vast and intricate world of chemistry, atoms are the building blocks of matter. These tiny particles are in constant motion, interacting with each other in various ways to form the molecules that make up everything around us. One of the most fundamental ways in which atoms interact is through the sharing of electrons, a process that gives rise to covalent bonds. In this article, we will delve into the world of covalent bonds, exploring what they are, how they form, and their significance in the world of chemistry.

Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bond that occurs when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons in order to achieve a stable electronic configuration. This type of bonding is typically seen in molecules, where atoms are bonded together through the sharing of electrons. The resulting molecule is held together by the attraction between the positively charged nuclei of the atoms and the negatively charged electrons that are shared between them.
What is a Covalent Bond?
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that forms when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This type of bonding is typically seen in molecules, where atoms are bonded together through the sharing of electrons. The resulting molecule is held together by the attraction between the positively charged nuclei of the atoms and the negatively charged electrons that are shared between them.
Covalent bonds are typically formed between non-metal atoms, such as carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen. These atoms tend to share electrons in order to achieve a stable electronic configuration, which is often referred to as a noble gas configuration. The noble gas configuration is a stable arrangement of electrons that is characteristic of the noble gases, such as helium, neon, and argon.

Types of Covalent Bonds
There are several types of covalent bonds, including:
- Sigma (σ) bonds: These bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons in a head-on manner. Sigma bonds are typically strong and are often seen in single bonds.
- Pi (π) bonds: These bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons in a side-by-side manner. Pi bonds are typically weaker than sigma bonds and are often seen in double and triple bonds.
- Delta (δ) bonds: These bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons in a delta-like manner. Delta bonds are typically seen in transition metal complexes.
Polar Covalent Bonds
Polar covalent bonds are a type of covalent bond that forms when two atoms with different electronegativities share a pair of electrons. In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other.
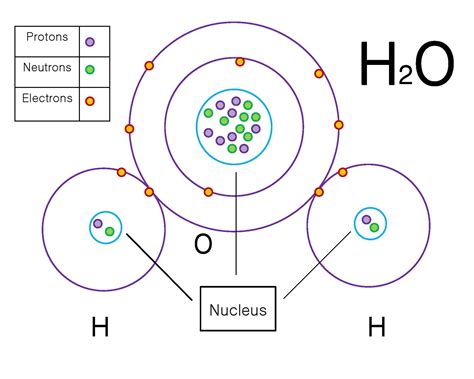
Polar covalent bonds are typically seen in molecules that contain atoms with different electronegativities, such as oxygen and hydrogen. In the molecule H2O, for example, the oxygen atom has a higher electronegativity than the hydrogen atoms, resulting in a polar covalent bond.

Properties of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds have several properties that are characteristic of this type of bonding. Some of the most important properties of covalent bonds include:
- Bond length: The distance between the nuclei of the two atoms that are bonded together.
- Bond strength: The energy required to break a covalent bond.
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
- Polarity: The distribution of electrons within a covalent bond.

Importance of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are essential for the formation of molecules, which are the building blocks of all matter. Without covalent bonds, molecules would not be able to form, and life as we know it would not be possible.
Covalent bonds are also important in many areas of chemistry, including organic chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. In organic chemistry, covalent bonds are used to form the complex molecules that are found in living organisms. In biochemistry, covalent bonds are used to form the molecules that make up biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA. In materials science, covalent bonds are used to form the materials that make up everything from plastics to metals.

Real-World Applications of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds have many real-world applications, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Covalent bonds are used to form the complex molecules that make up many pharmaceuticals.
- Materials science: Covalent bonds are used to form the materials that make up everything from plastics to metals.
- Energy storage: Covalent bonds are used to form the molecules that make up many energy storage devices, such as batteries.
- Biotechnology: Covalent bonds are used to form the molecules that make up many biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA.

We hope this article has helped you understand the importance of covalent bonds in the world of chemistry. From the formation of molecules to the creation of complex materials, covalent bonds play a crucial role in many areas of science and technology. Whether you're a student of chemistry or simply interested in learning more about the world around you, we hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of covalent bonds.
What is a covalent bond?
+A covalent bond is a chemical bond that forms when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons in order to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
What are the different types of covalent bonds?
+There are several types of covalent bonds, including sigma (σ) bonds, pi (π) bonds, and delta (δ) bonds.
What is the importance of covalent bonds in chemistry?
+Covalent bonds are essential for the formation of molecules, which are the building blocks of all matter. Without covalent bonds, molecules would not be able to form, and life as we know it would not be possible.