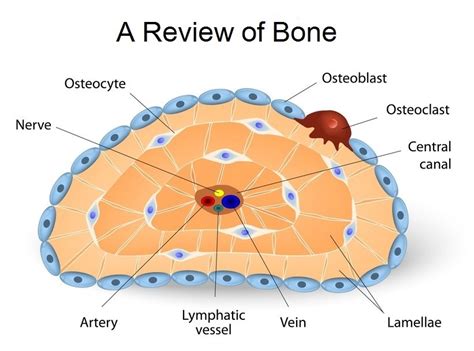
The fascinating world of bone formation! The process by which our bodies create the framework that supports us is a complex and highly regulated process. At the heart of this process are two types of cells: chondrocytes and osteocytes. These cells work together to form bone tissue, which is essential for our movement, protection, and overall health. In this article, we will delve into the six ways that chondrocytes and osteocytes form bone tissue, exploring the intricacies of bone formation and the crucial roles that these cells play.
Understanding Chondrocytes and Osteocytes
Before we dive into the six ways that chondrocytes and osteocytes form bone tissue, it's essential to understand what these cells are and what they do. Chondrocytes are cells found in healthy cartilage and are responsible for producing and maintaining the cartilaginous matrix. They are the only cells found in healthy cartilage and are essential for the growth and development of cartilage tissue.
Osteocytes, on the other hand, are cells found in bone tissue and are responsible for maintaining the bone matrix. They are the most abundant cell type in bone and play a crucial role in regulating bone remodeling and density.

1. Chondrocytes Produce Cartilage Matrix
The first step in bone formation is the production of cartilage matrix by chondrocytes. Chondrocytes produce a cartilaginous matrix that provides a framework for bone growth. This matrix is composed of collagen, proteoglycans, and other molecules that provide structure and support to the developing bone.
Chondrocytes and Cartilage Matrix Production
Chondrocytes produce cartilage matrix through a process called endochondral ossification. During this process, chondrocytes differentiate and mature, producing a cartilaginous matrix that is rich in collagen and proteoglycans. This matrix provides a scaffold for bone growth and is essential for the development of bone tissue.
2. Osteocytes Regulate Bone Remodeling
Osteocytes play a crucial role in regulating bone remodeling, which is the process by which old bone tissue is replaced with new tissue. Osteocytes regulate bone remodeling by responding to mechanical stress and hormonal signals. They produce signals that activate osteoclasts, which are cells that break down bone tissue, and osteoblasts, which are cells that build new bone tissue.

3. Chondrocytes Differentiate into Osteoblasts
As bone growth progresses, chondrocytes differentiate into osteoblasts. Osteoblasts are cells that produce bone matrix and are responsible for bone mineralization. During this process, chondrocytes undergo a series of changes, including changes in gene expression and cell morphology.
Chondrocytes and Osteoblast Differentiation
Chondrocytes differentiate into osteoblasts through a process called chondrocyte hypertrophy. During this process, chondrocytes increase in size and produce a matrix that is rich in collagen and proteoglycans. This matrix provides a scaffold for bone growth and is essential for the development of bone tissue.
4. Osteocytes Produce Bone Matrix
Osteocytes produce bone matrix through a process called osteogenesis. During this process, osteocytes produce a matrix that is rich in collagen and minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus. This matrix provides a framework for bone growth and is essential for the development of bone tissue.

5. Chondrocytes and Osteocytes Interact to Regulate Bone Growth
Chondrocytes and osteocytes interact to regulate bone growth. Chondrocytes produce signals that activate osteoblasts, which produce bone matrix. Osteocytes, in turn, produce signals that regulate osteoclast activity, which is essential for bone remodeling.
Chondrocytes and Osteocytes Interaction
Chondrocytes and osteocytes interact through a complex network of signals and pathways. These interactions are essential for regulating bone growth and development. Chondrocytes produce signals that activate osteoblasts, which produce bone matrix. Osteocytes, in turn, produce signals that regulate osteoclast activity, which is essential for bone remodeling.
6. Osteocytes Maintain Bone Density
Finally, osteocytes play a crucial role in maintaining bone density. Osteocytes regulate bone remodeling by responding to mechanical stress and hormonal signals. They produce signals that activate osteoclasts, which break down bone tissue, and osteoblasts, which build new bone tissue.

In conclusion, the formation of bone tissue is a complex process that involves the coordinated efforts of chondrocytes and osteocytes. These cells work together to produce a framework that supports our bodies and enables us to move and function. By understanding the six ways that chondrocytes and osteocytes form bone tissue, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate processes that occur in our bodies and develop new treatments for bone-related disorders.
What is the role of chondrocytes in bone formation?
+Chondrocytes play a crucial role in bone formation by producing cartilage matrix, which provides a framework for bone growth.
How do osteocytes regulate bone remodeling?
+Osteocytes regulate bone remodeling by responding to mechanical stress and hormonal signals. They produce signals that activate osteoclasts, which break down bone tissue, and osteoblasts, which build new bone tissue.
What is the importance of chondrocytes and osteocytes interaction in bone growth?
+The interaction between chondrocytes and osteocytes is essential for regulating bone growth and development. Chondrocytes produce signals that activate osteoblasts, which produce bone matrix. Osteocytes, in turn, produce signals that regulate osteoclast activity, which is essential for bone remodeling.