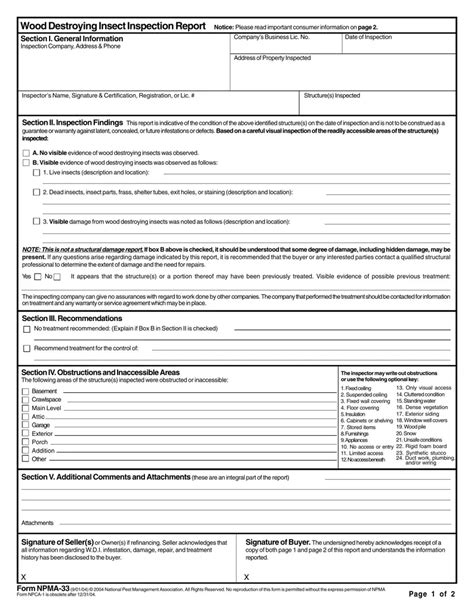
Mastering Form NPMA-33 is a crucial step for pest management professionals looking to demonstrate their expertise and commitment to providing high-quality services. The NPMA-33 form, also known as the Wood-Destroying Insect (WDI) Inspection Report, is a standardized document used to report on the presence or absence of wood-destroying insects and other conditions that may affect the integrity of a structure. In this article, we will break down the process of mastering Form NPMA-33 into 5 easy steps, providing you with a comprehensive guide to help you improve your skills and confidence.
Step 1: Understanding the Purpose and Scope of Form NPMA-33

The NPMA-33 form is designed to provide a clear and concise report on the results of a wood-destroying insect inspection. The form is typically used for real estate transactions, but it can also be used for other purposes, such as identifying potential issues in existing structures. To master Form NPMA-33, it's essential to understand its purpose and scope. The form is divided into several sections, including:
- General Information: This section includes details about the property, including the address, inspection date, and inspector's information.
- Inspection Summary: This section provides a brief overview of the inspection findings, including the presence or absence of wood-destroying insects and other conditions.
- Inspection Details: This section provides a detailed report on the inspection findings, including notes on the condition of the structure and any evidence of wood-destroying insects.
Key Components of Form NPMA-33
To effectively complete Form NPMA-33, it's crucial to understand the key components, including:
- Wood-destroying insects: This includes termites, carpenter ants, and other insects that can cause significant damage to structures.
- Conditions conducive to infestation: This includes factors that can contribute to the presence of wood-destroying insects, such as moisture, debris, and poor ventilation.
- Recommendations: This section provides suggestions for addressing any issues identified during the inspection.
Step 2: Conducting a Thorough Inspection

Conducting a thorough inspection is critical to completing Form NPMA-33 accurately. The inspection should include a visual examination of the structure, including the foundation, walls, roof, and any other areas that may be susceptible to wood-destroying insects. The inspector should also look for conditions conducive to infestation, such as moisture, debris, and poor ventilation.
Inspection Tools and Techniques
To conduct a thorough inspection, the following tools and techniques may be used:
- Flashlight: To illuminate dark areas and inspect for signs of wood-destroying insects.
- Moisture meter: To detect moisture levels in the structure, which can contribute to infestation.
- Probing tools: To inspect for signs of damage or infestation in areas that are difficult to access.
Step 3: Identifying Wood-Destroying Insects and Conditions

Identifying wood-destroying insects and conditions is a critical component of completing Form NPMA-33. The inspector should be able to recognize the signs of infestation, including:
- Live insects: Termites, carpenter ants, and other wood-destroying insects.
- Damage: Signs of damage, such as tunneling, galleries, and discoloration.
- Droppings: Insect droppings, such as frass, which can indicate the presence of wood-destroying insects.
Common Wood-Destroying Insects
Some common wood-destroying insects include:
- Termites: These are one of the most common wood-destroying insects, and can cause significant damage to structures.
- Carpenter ants: These ants can cause damage to structures by excavating wood to create nests.
- Powderpost beetles: These beetles can cause damage to wood by creating tunnels and galleries.
Step 4: Completing Form NPMA-33

Once the inspection is complete, the inspector can begin completing Form NPMA-33. The form should include all relevant information, including:
- General information: Property details, inspection date, and inspector's information.
- Inspection summary: A brief overview of the inspection findings.
- Inspection details: A detailed report on the inspection findings, including notes on the condition of the structure and any evidence of wood-destroying insects.
Tips for Completing Form NPMA-33
To ensure that Form NPMA-33 is completed accurately, the following tips should be followed:
- Use clear and concise language.
- Include all relevant information.
- Use diagrams and sketches to illustrate findings.
- Proofread the form carefully to ensure accuracy.
Step 5: Reviewing and Finalizing Form NPMA-33

Once Form NPMA-33 is complete, it's essential to review and finalize the document. The inspector should carefully review the form to ensure that all information is accurate and complete.
Quality Control Checks
To ensure that Form NPMA-33 is accurate and complete, the following quality control checks should be performed:
- Review the form for completeness and accuracy.
- Check for spelling and grammatical errors.
- Verify that all required information is included.
By following these 5 easy steps, pest management professionals can master Form NPMA-33 and provide high-quality services to their clients. Remember to always follow the guidelines and regulations outlined by the National Pest Management Association (NPMA) and other relevant authorities.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to mastering Form NPMA-33. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your colleagues and friends to help them improve their skills and knowledge.
What is Form NPMA-33?
+Form NPMA-33 is a standardized document used to report on the presence or absence of wood-destroying insects and other conditions that may affect the integrity of a structure.
What is the purpose of Form NPMA-33?
+The purpose of Form NPMA-33 is to provide a clear and concise report on the results of a wood-destroying insect inspection.
How do I complete Form NPMA-33?
+To complete Form NPMA-33, follow the 5 easy steps outlined in this article, including understanding the purpose and scope of the form, conducting a thorough inspection, identifying wood-destroying insects and conditions, completing the form, and reviewing and finalizing the document.