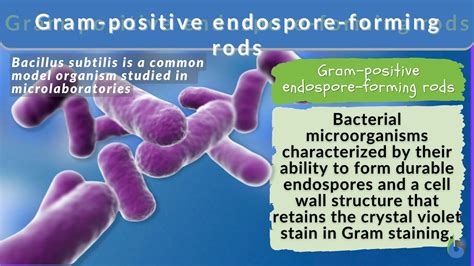
Gram-negative bacteria are a diverse group of microorganisms that are characterized by the presence of a thin peptidoglycan layer in their cell walls, which is sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. This structural feature distinguishes them from Gram-positive bacteria, which have a thicker peptidoglycan layer. One of the key differences between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is their ability to form endospores.
Endospores are highly resistant, dormant structures formed by some bacteria as a survival mechanism. They are designed to withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as high temperatures, desiccation, and chemical disinfectants. Endospore formation is a complex process that involves a series of cellular and molecular changes, ultimately leading to the creation of a highly resistant spore.
Do Gram-Negative Bacteria Form Endospores?

In general, Gram-negative bacteria do not form endospores. Endospore formation is typically associated with Gram-positive bacteria, such as those belonging to the genera Bacillus and Clostridium. These bacteria have a unique cell wall structure that allows them to form endospores, which are highly resistant to environmental stresses.
However, there are some exceptions among Gram-negative bacteria. A few species, such as those belonging to the genus Azotobacter, have been reported to form cyst-like structures that resemble endospores. These structures, known as cysts or azotocysts, are highly resistant to environmental stresses and can survive for extended periods in a dormant state.
Exceptions Among Gram-Negative Bacteria
While Gram-negative bacteria do not typically form endospores, there are some exceptions. For example:- Azotobacter: As mentioned earlier, some species of Azotobacter form cyst-like structures that resemble endospores. These structures are highly resistant to environmental stresses and can survive for extended periods in a dormant state.
- Rhodopseudomonas: Some species of Rhodopseudomonas, a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, have been reported to form endospore-like structures. However, these structures are not as highly resistant as those formed by Gram-positive bacteria.
It is essential to note that these exceptions are relatively rare among Gram-negative bacteria, and endospore formation is not a characteristic feature of this group.
Why Don't Gram-Negative Bacteria Form Endospores?

There are several reasons why Gram-negative bacteria do not typically form endospores:
- Cell wall structure: Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer in their cell walls, which is not conducive to endospore formation. Endospore formation requires a thicker peptidoglycan layer, which is characteristic of Gram-positive bacteria.
- Lack of sporulation genes: Gram-negative bacteria typically lack the genes necessary for sporulation, which is the process of endospore formation.
- Alternative survival mechanisms: Gram-negative bacteria have evolved alternative survival mechanisms, such as biofilm formation and quorum sensing, which allow them to survive in a variety of environments.
Implications of Endospore Formation in Gram-Negative Bacteria
The ability of some Gram-negative bacteria to form endospore-like structures has significant implications for our understanding of bacterial survival mechanisms. For example:- Enhanced resistance: Endospore-like structures formed by Gram-negative bacteria can provide enhanced resistance to environmental stresses, such as heat, desiccation, and chemical disinfectants.
- New targets for antimicrobial therapy: The discovery of endospore-like structures in Gram-negative bacteria may provide new targets for antimicrobial therapy, such as developing drugs that target sporulation genes.
In conclusion, while Gram-negative bacteria do not typically form endospores, there are some exceptions among certain species. Understanding the mechanisms of endospore formation in Gram-negative bacteria can provide insights into bacterial survival mechanisms and may have significant implications for antimicrobial therapy.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of endospore formation in Gram-negative bacteria. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is the main difference between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria?
+The main difference between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is the structure of their cell walls. Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer, while Gram-positive bacteria have a thicker peptidoglycan layer.
Do all Gram-negative bacteria form endospores?
+No, not all Gram-negative bacteria form endospores. Endospore formation is typically associated with Gram-positive bacteria, but there are some exceptions among certain Gram-negative species.
What are the implications of endospore formation in Gram-negative bacteria?
+The ability of some Gram-negative bacteria to form endospore-like structures has significant implications for our understanding of bacterial survival mechanisms and may provide new targets for antimicrobial therapy.