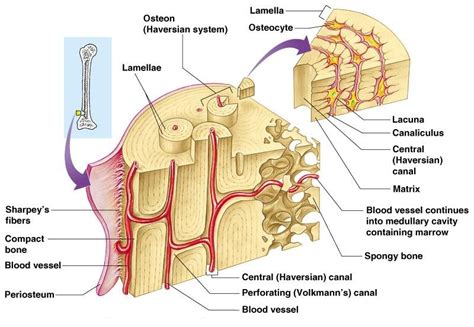
Bone cells, also known as osteocytes, play a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of our skeletal system. One of the most fascinating aspects of bone cells is how they form around Haversian canals, which are tiny channels within the bone tissue that allow for the passage of blood vessels and nerve fibers. In this article, we will delve into the five ways bone cells form around Haversian canals, exploring the intricate processes that enable the development and maintenance of healthy bones.

Understanding Haversian Canals
Before we dive into the ways bone cells form around Haversian canals, it's essential to understand what these canals are and their significance in bone health. Haversian canals, also known as central canals, are tiny channels within compact bone tissue that house blood vessels, nerve fibers, and lymphatic vessels. These canals are crucial for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to bone cells and the removal of waste products.
Role of Haversian Canals in Bone Health
Haversian canals play a vital role in maintaining bone health by:
- Providing a pathway for blood vessels to supply oxygen and nutrients to bone cells
- Enabling the removal of waste products through lymphatic vessels
- Allowing nerve fibers to transmit signals that regulate bone growth and remodeling
- Facilitating the communication between bone cells and other tissues
5 Ways Bone Cells Form Around Haversian Canals
Now that we have a deeper understanding of Haversian canals, let's explore the five ways bone cells form around these canals.
1. Osteogenesis: The Birth of Bone Cells
Osteogenesis is the process by which bone cells, or osteocytes, are formed. During osteogenesis, mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into osteoblasts, which then mature into osteocytes. These osteocytes are embedded within the bone matrix, where they communicate with other bone cells and regulate bone growth and remodeling.

2. Bone Matrix Deposition
After osteocytes are formed, they begin to deposit bone matrix, a complex mixture of organic and inorganic compounds that provide the structural framework for bone tissue. The bone matrix is composed of collagen fibers, hydroxyapatite crystals, and other proteins, which are deposited around the Haversian canals.
3. Mineralization of Bone Matrix
As the bone matrix is deposited, it undergoes mineralization, a process in which hydroxyapatite crystals are deposited within the matrix. Mineralization is essential for the development of bone strength and rigidity, allowing bones to withstand mechanical stress.
4. Osteoclast-Mediated Resorption
Osteoclasts are specialized bone cells that play a critical role in bone remodeling by resorbing bone tissue. Osteoclasts secrete enzymes and acids that break down the bone matrix, releasing minerals and other compounds into the bloodstream. This process allows for the removal of old or damaged bone tissue, making way for new bone growth.

5. Bone Remodeling and Adaptation
Bone remodeling is a continuous process that involves the resorption and formation of bone tissue. As bones undergo mechanical stress, osteocytes and other bone cells adapt to the changing loads by remodeling the bone tissue. This adaptation enables bones to maintain their strength and function, even in the face of changing demands.

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the formation of bone cells around Haversian canals is a complex and highly regulated process that involves multiple cell types and signaling pathways. Understanding these processes is essential for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for bone diseases and disorders. Future research should focus on elucidating the molecular mechanisms that regulate bone cell formation and function, with the ultimate goal of improving bone health and preventing skeletal disorders.
Takeaways and Recommendations
- Haversian canals play a critical role in bone health by providing a pathway for blood vessels, nerve fibers, and lymphatic vessels.
- Bone cells, or osteocytes, form around Haversian canals through a complex process involving osteogenesis, bone matrix deposition, mineralization, osteoclast-mediated resorption, and bone remodeling.
- Understanding the molecular mechanisms that regulate bone cell formation and function is essential for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for bone diseases and disorders.
- Future research should focus on elucidating the molecular mechanisms that regulate bone cell formation and function, with the ultimate goal of improving bone health and preventing skeletal disorders.

What is the role of Haversian canals in bone health?
+Haversian canals play a crucial role in bone health by providing a pathway for blood vessels, nerve fibers, and lymphatic vessels. They enable the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to bone cells and the removal of waste products.
What is osteogenesis?
+Osteogenesis is the process by which bone cells, or osteocytes, are formed. During osteogenesis, mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into osteoblasts, which then mature into osteocytes.
What is the significance of bone remodeling in bone health?
+Bone remodeling is a continuous process that involves the resorption and formation of bone tissue. This adaptation enables bones to maintain their strength and function, even in the face of changing demands.