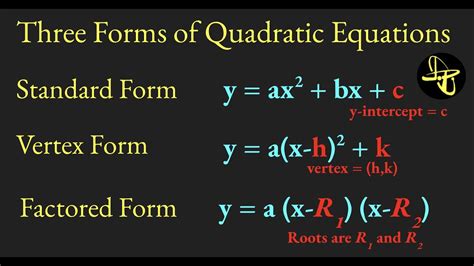
Quadratic equations are a fundamental concept in mathematics, and being able to write them in different forms is an essential skill for problem-solving. A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree two, which means the highest power of the variable (usually x) is two. In this article, we will explore three ways to write a quadratic equation, including the standard form, factored form, and vertex form.
What is a Quadratic Equation?

A quadratic equation is a mathematical equation that can be written in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and x is the variable. The equation can be solved for x, and the solutions are called the roots or zeros of the equation. Quadratic equations are used to model real-world problems in physics, engineering, economics, and other fields.
Standard Form: ax^2 + bx + c = 0

The standard form of a quadratic equation is ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and x is the variable. This is the most common form of a quadratic equation and is often used to solve problems. For example, the equation x^2 + 5x + 6 = 0 is in standard form. To write a quadratic equation in standard form, we need to know the values of a, b, and c.
How to Write a Quadratic Equation in Standard Form
To write a quadratic equation in standard form, follow these steps:
- Write the equation in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0.
- Identify the values of a, b, and c.
- Plug in the values of a, b, and c into the equation.
For example, if we want to write the equation x^2 + 5x + 6 = 0 in standard form, we can identify the values of a, b, and c as a = 1, b = 5, and c = 6.
Factored Form: (x - r)(x - s) = 0

The factored form of a quadratic equation is (x - r)(x - s) = 0, where r and s are the roots or zeros of the equation. This form is useful for solving quadratic equations by factoring. For example, the equation (x - 2)(x + 3) = 0 is in factored form.
How to Write a Quadratic Equation in Factored Form
To write a quadratic equation in factored form, follow these steps:
- Find the roots or zeros of the equation.
- Write the equation in the form (x - r)(x - s) = 0, where r and s are the roots.
For example, if we want to write the equation x^2 + 5x + 6 = 0 in factored form, we can find the roots as x = -2 and x = -3. Then, we can write the equation as (x + 2)(x + 3) = 0.
Vertex Form: a(x - h)^2 + k = 0

The vertex form of a quadratic equation is a(x - h)^2 + k = 0, where (h, k) is the vertex of the parabola. This form is useful for graphing quadratic equations and finding the vertex of the parabola. For example, the equation (x - 2)^2 + 3 = 0 is in vertex form.
How to Write a Quadratic Equation in Vertex Form
To write a quadratic equation in vertex form, follow these steps:
- Find the vertex of the parabola.
- Write the equation in the form a(x - h)^2 + k = 0, where (h, k) is the vertex.
For example, if we want to write the equation x^2 + 5x + 6 = 0 in vertex form, we can find the vertex as (h, k) = (-2, -1). Then, we can write the equation as (x + 2)^2 - 1 = 0.
In conclusion, quadratic equations can be written in three forms: standard form, factored form, and vertex form. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages, and being able to write a quadratic equation in different forms is an essential skill for problem-solving. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can write a quadratic equation in any of these forms.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any questions or need further clarification, please don't hesitate to ask.
What is a quadratic equation?
+A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree two, which means the highest power of the variable (usually x) is two.
What are the three forms of a quadratic equation?
+The three forms of a quadratic equation are standard form (ax^2 + bx + c = 0), factored form ((x - r)(x - s) = 0), and vertex form (a(x - h)^2 + k = 0).
How do I write a quadratic equation in standard form?
+To write a quadratic equation in standard form, identify the values of a, b, and c, and plug them into the equation ax^2 + bx + c = 0.