The concept of ions is fundamental to understanding chemistry, and it's essential to grasp why elements form ions to appreciate the intricacies of chemical reactions and bonding. In this article, we'll delve into the world of ions, exploring the reasons behind their formation, the types of ions, and the significance of ions in chemistry.

What are Ions?
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. This process is known as ionization. Ions can be either cations (positively charged) or anions (negatively charged). The formation of ions is crucial in chemistry, as it enables the creation of chemical bonds and the facilitation of chemical reactions.
Why Do Elements Form Ions?
Elements form ions to achieve a more stable electronic configuration, often referred to as a noble gas configuration. Noble gases, such as helium, neon, and argon, have a full outer energy level, which makes them chemically inert. Elements tend to form ions to mimic this stability by gaining or losing electrons to complete their outer energy level.
There are several reasons why elements form ions:
- Electron configuration: Elements strive to achieve a noble gas configuration by gaining or losing electrons. This results in a more stable electronic arrangement, which is essential for the element's chemical behavior.
- Chemical bonding: Ions participate in chemical bonding by attracting oppositely charged ions. This attraction leads to the formation of ionic compounds, which are essential in chemistry.
- Reactivity: Ions can exhibit unique reactivity, which is critical in various chemical reactions. For instance, cations can act as Lewis acids, while anions can act as Lewis bases.
- Thermodynamic stability: Ion formation can lead to a more thermodynamically stable state, as the energy required to form ions is often lower than the energy released during the reaction.
Types of Ions
There are two primary types of ions: cations and anions.

Cations
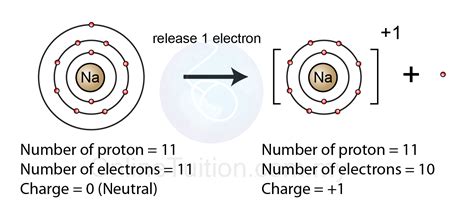
Cations are positively charged ions formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. This process is known as oxidation. Cations are typically formed by metals, which tend to lose electrons to achieve a more stable electronic configuration.
Examples of cations include:
- Sodium ion (Na+)
- Calcium ion (Ca2+)
- Aluminum ion (Al3+)
Anions
Anions are negatively charged ions formed when an atom gains one or more electrons. This process is known as reduction. Anions are typically formed by nonmetals, which tend to gain electrons to achieve a more stable electronic configuration.
Examples of anions include:
- Chloride ion (Cl-)
- Oxygen ion (O2-)
- Nitride ion (N3-)
Significance of Ions in Chemistry
Ions play a crucial role in chemistry, as they participate in various chemical reactions and bonding. Some of the significance of ions in chemistry includes:
- Chemical bonding: Ions are essential for the formation of ionic compounds, which are common in chemistry.
- Reactivity: Ions can exhibit unique reactivity, which is critical in various chemical reactions.
- pH and acid-base chemistry: Ions are involved in acid-base reactions, which are essential in understanding pH and chemical reactivity.
- Biochemistry: Ions are vital in biological systems, where they participate in various biochemical reactions and processes.

Real-World Applications of Ions
Ions have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Electrochemistry: Ions are essential in electrochemical reactions, which are used in batteries, fuel cells, and electrolysis.
- Medicine: Ions are vital in biological systems, where they participate in various biochemical reactions and processes.
- Environmental science: Ions are involved in various environmental processes, such as acid rain and water treatment.
- Materials science: Ions are used in the development of materials, such as semiconductors and ceramics.

Conclusion: The Importance of Ions in Chemistry
In conclusion, ions are a fundamental aspect of chemistry, and understanding why elements form ions is essential for appreciating the intricacies of chemical reactions and bonding. Ions participate in various chemical reactions, exhibit unique reactivity, and are crucial in real-world applications. By grasping the concept of ions, we can better understand the world around us and develop new technologies and materials.
What is the main reason why elements form ions?
+Elements form ions to achieve a more stable electronic configuration, often referred to as a noble gas configuration.
What are the two primary types of ions?
+The two primary types of ions are cations (positively charged) and anions (negatively charged).
What is the significance of ions in chemistry?
+Ions are essential for chemical bonding, reactivity, pH and acid-base chemistry, and biochemical reactions.