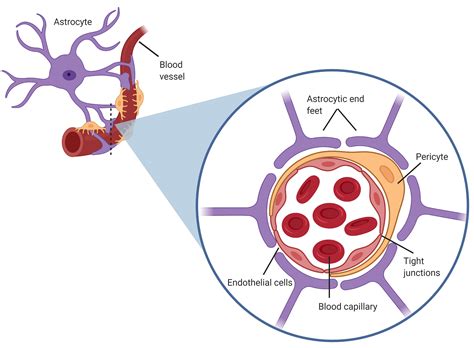
The human brain is a complex and intricate organ, comprising billions of neurons that facilitate various cognitive functions. To protect this vital organ from harm, the body has developed a specialized barrier known as the blood-brain barrier (BBB). This barrier is formed by a unique group of cells called astrocytes, which play a crucial role in maintaining the brain's health and function.
The blood-brain barrier is a highly selective permeable barrier that separates the brain from the bloodstream. It is composed of endothelial cells that line the blood vessels, pericytes that surround the blood vessels, and astrocytes that extend their foot processes to cover the blood vessels. Astrocytes are the most important component of the BBB, as they regulate the passage of molecules and ions between the blood and the brain.

Astrocytes Form The Blood Brain Barrier
Structure and Function of Astrocytes
Astrocytes are a type of glial cell that are found throughout the central nervous system (CNS). They are characterized by their star-shaped morphology, with multiple processes that extend from the cell body to interact with neurons, blood vessels, and other glial cells. Astrocytes play a crucial role in maintaining the brain's homeostasis, regulating the concentration of ions and neurotransmitters, and providing nutrients and oxygen to neurons.
Astrocytes have several key functions that contribute to the formation and maintenance of the BBB:
- Regulation of ion and water balance: Astrocytes regulate the concentration of ions and water in the brain by controlling the passage of these molecules across the BBB.
- Maintenance of neurotransmitter levels: Astrocytes regulate the levels of neurotransmitters, such as glutamate and GABA, by removing excess neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft.
- Supply of nutrients and oxygen: Astrocytes provide nutrients and oxygen to neurons by regulating the passage of these molecules across the BBB.
- Removal of waste products: Astrocytes remove waste products, such as beta-amyloid peptides, from the brain by transporting them across the BBB.
Astrocytes and the Blood-Brain Barrier
Astrocytes play a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of the BBB. They extend their foot processes to cover the blood vessels, forming a tight seal that restricts the passage of molecules and ions between the blood and the brain. Astrocytes also regulate the expression of tight junction proteins, such as occludin and claudin, which are essential for maintaining the integrity of the BBB.
Astrocytes also interact with pericytes and endothelial cells to regulate the passage of molecules and ions across the BBB. They release factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), that stimulate the growth and differentiation of endothelial cells, which form the inner lining of blood vessels.

Role of Astrocytes in Neurological Disorders
Astrocytes play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of various neurological disorders, including:
- Alzheimer's disease: Astrocytes are involved in the removal of beta-amyloid peptides, which are toxic to neurons and contribute to the development of Alzheimer's disease.
- Stroke: Astrocytes play a crucial role in the repair of damaged brain tissue after stroke by regulating the expression of genes involved in inflammation and tissue repair.
- Multiple sclerosis: Astrocytes are involved in the repair of damaged myelin, which is essential for the transmission of nerve impulses.
Astrocytes as a Therapeutic Target
Astrocytes are a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of various neurological disorders. Strategies that target astrocytes, such as astrocyte transplantation and gene therapy, are being developed to promote brain repair and regeneration.
Astrocyte transplantation involves the transplantation of healthy astrocytes into damaged brain tissue to promote repair and regeneration. Gene therapy involves the delivery of genes that promote the expression of beneficial factors, such as VEGF, to stimulate the growth and differentiation of endothelial cells.

Conclusion
Astrocytes play a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier, regulating the passage of molecules and ions between the blood and the brain. They are involved in various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and multiple sclerosis. Strategies that target astrocytes, such as astrocyte transplantation and gene therapy, are being developed to promote brain repair and regeneration.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of astrocytes in maintaining brain health. How do you think astrocytes can be targeted to promote brain repair and regeneration?
What is the main function of astrocytes in the brain?
+Astrocytes play a crucial role in maintaining the brain's homeostasis, regulating the concentration of ions and neurotransmitters, and providing nutrients and oxygen to neurons.
How do astrocytes contribute to the formation of the blood-brain barrier?
+Astrocytes extend their foot processes to cover the blood vessels, forming a tight seal that restricts the passage of molecules and ions between the blood and the brain.
What is the role of astrocytes in neurological disorders?
+Astrocytes play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and multiple sclerosis.