Acidic compounds are a crucial aspect of chemistry, playing a vital role in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, and environmental science. In chemistry, an acidic compound is a molecule that donates a proton (H+ ion) or accepts an electron pair. These compounds are essential in understanding chemical reactions, biochemical processes, and the properties of matter.
Understanding the elements that form acidic compounds is vital in chemistry, as it enables chemists to predict the behavior of these compounds in different reactions and conditions. Acidic compounds are formed by the combination of specific elements, which are characterized by their ability to donate or accept electrons.
In this article, we will explore the elements that form acidic compounds, their properties, and the types of acidic compounds they form. We will also discuss the importance of acidic compounds in chemistry and their applications in various industries.
What are the Key Elements that Form Acidic Compounds?
Nonmetals and Acidic Compounds

Nonmetals are the primary elements that form acidic compounds. Nonmetals are elements that do not exhibit the properties of metals, such as luster, malleability, and ductility. They are typically found in the p-block of the periodic table and include elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and chlorine.
Nonmetals form acidic compounds by combining with hydrogen or other nonmetals. For example, when oxygen combines with hydrogen, it forms water (H2O), which is a weak acid. Similarly, when nitrogen combines with hydrogen, it forms ammonia (NH3), which is a weak base.
Halogen Family and Acidic Compounds
Halogens and Acidic Compounds

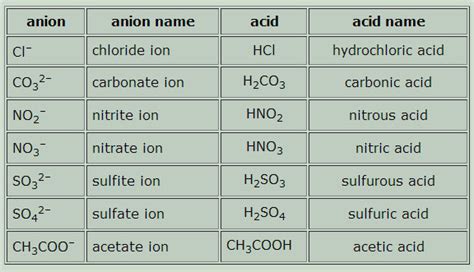
The halogen family, which includes elements such as fluorine, chlorine, and bromine, also forms acidic compounds. Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals that readily form ions with other elements. When halogens combine with hydrogen, they form strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hydrofluoric acid (HF).
Chalcogen Family and Acidic Compounds
Chalcogens and Acidic Compounds

The chalcogen family, which includes elements such as sulfur, selenium, and tellurium, also forms acidic compounds. Chalcogens are nonmetals that readily form ions with other elements. When chalcogens combine with hydrogen, they form weak acids, such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and hydrogen selenide (H2Se).
Properties of Acidic Compounds
Acidic compounds exhibit specific properties, including:
- pH: Acidic compounds have a pH below 7, indicating that they are acidic in nature.
- Corrosiveness: Acidic compounds can corrode metals and other materials.
- Reactivity: Acidic compounds readily react with other elements and compounds.
Types of Acidic Compounds
Acidic compounds can be classified into several types, including:
- Strong acids: These are acidic compounds that completely dissociate in water, releasing H+ ions. Examples include hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
- Weak acids: These are acidic compounds that partially dissociate in water, releasing H+ ions. Examples include acetic acid (CH3COOH) and citric acid (C6H8O7).
- Organic acids: These are acidic compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. Examples include acetic acid (CH3COOH) and oxalic acid (C2H2O4).
Importance of Acidic Compounds in Chemistry
Acidic compounds play a vital role in various industries, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Acidic compounds are used as active ingredients in medications, such as antacids and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Food: Acidic compounds are used as preservatives and flavor enhancers in food products, such as pickled vegetables and fruit juices.
- Environmental science: Acidic compounds are used to monitor and control the pH of water and soil in environmental science applications.
Applications of Acidic Compounds
Acidic compounds have various applications in different industries, including:
- Cleaning agents: Acidic compounds are used as cleaning agents in industries, such as textiles and manufacturing.
- Pharmaceuticals: Acidic compounds are used as active ingredients in medications, such as antacids and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Food processing: Acidic compounds are used as preservatives and flavor enhancers in food products, such as pickled vegetables and fruit juices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, acidic compounds are formed by the combination of specific elements, including nonmetals, halogens, and chalcogens. These compounds exhibit specific properties, including pH, corrosiveness, and reactivity. Acidic compounds are essential in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, and environmental science.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the elements that form acidic compounds and their applications in different industries. Share your thoughts and comments below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are acidic compounds?
+Acidic compounds are molecules that donate a proton (H+ ion) or accept an electron pair.
What are the key elements that form acidic compounds?
+Nonmetals, halogens, and chalcogens are the key elements that form acidic compounds.
What are the properties of acidic compounds?
+Acidic compounds exhibit specific properties, including pH, corrosiveness, and reactivity.