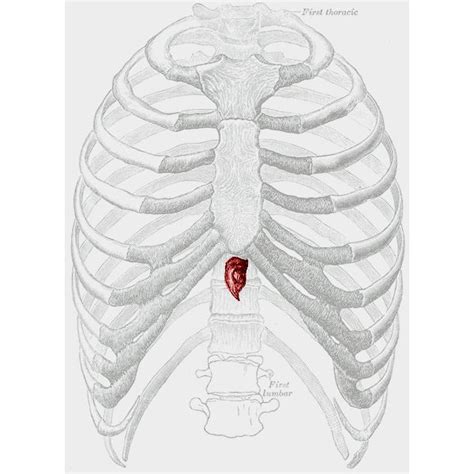
The xiphoid process, a small cartilaginous structure located at the bottom of the sternum, plays a vital role in the human respiratory system. While it may seem insignificant, this tiny structure is crucial in facilitating artificial respiration, a life-saving technique used to assist individuals who are having trouble breathing. In this article, we will explore the five ways the xiphoid process aids in artificial respiration.
The Importance of the Xiphoid Process in Artificial Respiration

The xiphoid process serves as a landmark for healthcare professionals to locate the correct position for compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Its prominence at the bottom of the sternum provides a clear indication of the ribcage's position, allowing for accurate placement of the hands. This accuracy is crucial in ensuring effective chest compressions, which are essential for artificial respiration.
Locating the Xiphoid Process for Effective Compressions
To locate the xiphoid process, healthcare professionals typically start by feeling for the notch at the top of the sternum, known as the jugular notch. From there, they move their fingers down the sternum until they reach the xiphoid process, which is usually felt as a slight bump or protrusion. Once the xiphoid process is located, the healthcare professional can position their hands correctly for chest compressions.
Stabilizing the Chest Cavity

The xiphoid process helps to stabilize the chest cavity during artificial respiration. When chest compressions are applied, the xiphoid process acts as a fulcrum, allowing the sternum to pivot and enabling the lungs to expand and contract. This stabilization ensures that the chest cavity remains intact, facilitating effective breathing and oxygenation of the blood.
The Role of the Xiphoid Process in Facilitating Lung Expansion
During artificial respiration, the xiphoid process plays a crucial role in facilitating lung expansion. As the chest is compressed, the xiphoid process helps to ensure that the lungs expand and contract properly, allowing for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. This process is essential for maintaining adequate oxygenation of the blood and preventing tissue damage.
Assisting in the Maintenance of Proper Posture

The xiphoid process also assists in maintaining proper posture during artificial respiration. When the chest is compressed, the xiphoid process helps to maintain the natural curvature of the spine, ensuring that the lungs and diaphragm can function properly. This is particularly important in ensuring that the individual receiving artificial respiration is able to breathe effectively and maintain adequate oxygenation.
The Importance of Proper Posture in Artificial Respiration
Maintaining proper posture during artificial respiration is essential for ensuring effective breathing and oxygenation. When the individual receiving artificial respiration is positioned correctly, the xiphoid process helps to maintain the natural curvature of the spine, allowing the lungs and diaphragm to function properly. This is critical in preventing complications such as respiratory failure and ensuring the best possible outcome for the individual.
Providing a Landmark for Decompression

The xiphoid process serves as a landmark for decompression during artificial respiration. When the chest is decompressed, the xiphoid process helps to ensure that the lungs return to their normal position, allowing for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. This process is essential for maintaining adequate oxygenation of the blood and preventing tissue damage.
The Role of the Xiphoid Process in Decompression
During decompression, the xiphoid process plays a crucial role in ensuring that the lungs return to their normal position. As the chest is decompressed, the xiphoid process helps to facilitate the expansion of the lungs, allowing for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. This process is essential for maintaining adequate oxygenation of the blood and preventing complications such as respiratory failure.
Facilitating the Coordination of Breathing and Circulation

The xiphoid process facilitates the coordination of breathing and circulation during artificial respiration. As the chest is compressed and decompressed, the xiphoid process helps to ensure that the lungs and heart function properly, allowing for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide and the maintenance of adequate circulation. This coordination is essential for ensuring the best possible outcome for the individual receiving artificial respiration.
The Importance of Coordination in Artificial Respiration
The coordination of breathing and circulation is critical during artificial respiration. When the xiphoid process is functioning properly, it helps to ensure that the lungs and heart function in harmony, allowing for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide and the maintenance of adequate circulation. This coordination is essential for preventing complications such as respiratory failure and ensuring the best possible outcome for the individual.
In conclusion, the xiphoid process plays a vital role in facilitating artificial respiration. Its prominence at the bottom of the sternum provides a clear indication of the ribcage's position, allowing for accurate placement of the hands during chest compressions. The xiphoid process also helps to stabilize the chest cavity, facilitate lung expansion, assist in maintaining proper posture, provide a landmark for decompression, and facilitate the coordination of breathing and circulation. By understanding the importance of the xiphoid process in artificial respiration, healthcare professionals can provide more effective care and improve outcomes for individuals in need of this life-saving technique.
What is the xiphoid process?
+The xiphoid process is a small cartilaginous structure located at the bottom of the sternum.
What is the role of the xiphoid process in artificial respiration?
+The xiphoid process plays a vital role in facilitating artificial respiration by providing a landmark for compressions, stabilizing the chest cavity, facilitating lung expansion, assisting in maintaining proper posture, providing a landmark for decompression, and facilitating the coordination of breathing and circulation.
How is the xiphoid process located during artificial respiration?
+The xiphoid process is typically located by feeling for the notch at the top of the sternum, known as the jugular notch, and then moving the fingers down the sternum until the xiphoid process is felt as a slight bump or protrusion.