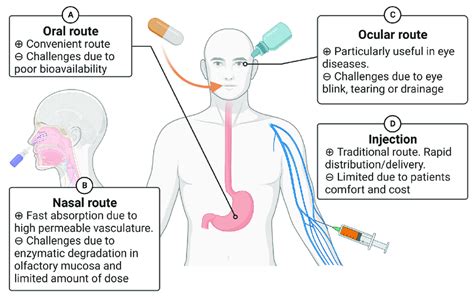
Intravenous (IV) therapy is a medical treatment that involves injecting fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into a patient's vein. This method of administration is widely used in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings to deliver essential treatments to patients who require immediate attention. The importance of IV therapy cannot be overstated, as it provides a rapid and efficient way to deliver medications, replenish fluids, and restore electrolyte balances.
IV therapy is often used in emergency situations, such as when a patient is experiencing severe dehydration, shock, or cardiac arrest. It is also used to administer medications that cannot be taken orally, such as antibiotics, painkillers, and chemotherapy agents. Additionally, IV therapy is used to provide nutritional support to patients who are unable to eat or digest food normally. With the increasing demand for IV therapy, it is essential to understand the different types of IV dosage forms and administration methods.

Types of IV Dosage Forms
There are several types of IV dosage forms, each with its unique characteristics and uses. The most common types of IV dosage forms include:
1. Solutions
Solutions are the most common type of IV dosage form. They are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances, typically a solvent and a solute. Solutions can be further classified into several subtypes, including:
- Isotonic solutions: These solutions have the same concentration of solutes as human blood and are used to replenish fluids and electrolytes.
- Hypotonic solutions: These solutions have a lower concentration of solutes than human blood and are used to treat dehydration.
- Hypertonic solutions: These solutions have a higher concentration of solutes than human blood and are used to treat conditions such as hypernatremia.

2. Suspensions
Suspensions are IV dosage forms that contain undissolved particles or solids. They are often used to administer medications that are not soluble in water, such as some antibiotics and antifungals. Suspensions are typically shaken well before administration to ensure that the particles are evenly distributed.

3. Emulsions
Emulsions are IV dosage forms that contain two or more immiscible liquids, such as oil and water. They are often used to administer medications that are not soluble in water, such as some anesthetics and analgesics. Emulsions are typically stable and do not require shaking before administration.

IV Administration Methods
There are several IV administration methods, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. The most common IV administration methods include:
1. Peripheral IV Administration
Peripheral IV administration involves inserting a needle or catheter into a peripheral vein, typically in the arm or hand. This method is commonly used for short-term IV therapy and is often used in outpatient settings.

2. Central IV Administration
Central IV administration involves inserting a catheter into a central vein, typically in the chest or neck. This method is commonly used for long-term IV therapy and is often used in inpatient settings.

3. Midline IV Administration
Midline IV administration involves inserting a catheter into a vein in the upper arm, typically between the elbow and shoulder. This method is commonly used for short-term to moderate-term IV therapy and is often used in outpatient settings.

Benefits of IV Therapy
IV therapy offers several benefits, including:
- Rapid administration of medications and fluids
- Improved bioavailability of medications
- Reduced risk of gastrointestinal side effects
- Enhanced nutritional support
- Increased patient comfort and convenience

Risks and Complications of IV Therapy
While IV therapy is generally safe and effective, there are some risks and complications associated with its use. These include:
- Infection and sepsis
- Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
- Nerve damage and neuropathy
- Fluid overload and electrolyte imbalances
- Medication errors and adverse reactions

Conclusion
In conclusion, IV therapy is a vital medical treatment that offers several benefits and advantages. Understanding the different types of IV dosage forms and administration methods is essential for healthcare professionals to provide effective and safe care to patients. While there are some risks and complications associated with IV therapy, these can be minimized by following proper protocols and guidelines.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of IV dosage forms and administration methods. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is IV therapy?
+IV therapy is a medical treatment that involves injecting fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into a patient's vein.
What are the benefits of IV therapy?
+IV therapy offers several benefits, including rapid administration of medications and fluids, improved bioavailability of medications, and enhanced nutritional support.
What are the risks and complications of IV therapy?
+While IV therapy is generally safe and effective, there are some risks and complications associated with its use, including infection and sepsis, phlebitis and thrombophlebitis, and medication errors and adverse reactions.