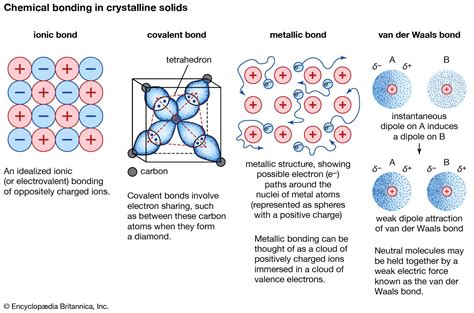
Understanding the Basics of Metallic Bonds

Metallic bonds are a type of chemical bond that is characteristic of metals. In this type of bond, the atoms release electrons to form a "sea of electrons" that surrounds the positively charged ions. This delocalization of electrons leads to the high malleability, ductility, and conductivity of metals. But which atoms are most likely to form metallic bonds?
The ability of an atom to form a metallic bond depends on its position in the periodic table. Atoms that are located on the left side of the periodic table, particularly in groups 1 and 2, are more likely to form metallic bonds. These atoms have a low number of electrons in their outermost energy level, which makes it easier for them to release electrons and form a positive ion.
Atoms in Group 1: The Alkali Metals
The alkali metals, which include lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr), are located in group 1 of the periodic table. These atoms have only one electron in their outermost energy level, which makes it very easy for them to release this electron and form a positive ion. As a result, the alkali metals are highly reactive and tend to lose one electron to form a +1 ion.
For example, sodium (Na) has an atomic number of 11 and an electron configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹. When sodium loses one electron, it forms a positive ion with a +1 charge, which is known as a sodium ion (Na⁺). This ion is highly reactive and can easily form metallic bonds with other atoms.
Atoms in Group 2: The Alkaline Earth Metals

The alkaline earth metals, which include beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra), are located in group 2 of the periodic table. These atoms have two electrons in their outermost energy level, which makes it relatively easy for them to release these electrons and form a positive ion.
For example, magnesium (Mg) has an atomic number of 12 and an electron configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s². When magnesium loses two electrons, it forms a positive ion with a +2 charge, which is known as a magnesium ion (Mg²⁺). This ion is highly reactive and can easily form metallic bonds with other atoms.
Other Atoms That Can Form Metallic Bonds
While the alkali and alkaline earth metals are the most likely to form metallic bonds, other atoms can also exhibit this type of bonding. For example, the transition metals, which include elements such as iron (Fe), copper (Cu), and silver (Ag), can form metallic bonds under certain conditions.
These atoms have a partially filled d subshell, which makes it possible for them to release electrons and form a positive ion. However, the transition metals tend to form ions with a +2 or +3 charge, which is different from the +1 charge of the alkali metals.
The Most Likely Atom to Form a Metallic Bond

Based on the position of the atoms in the periodic table and their electron configuration, caesium (Cs) is the most likely atom to form a metallic bond. Caesium is an alkali metal that has an atomic number of 55 and an electron configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶ 6s¹.
As an alkali metal, caesium has only one electron in its outermost energy level, which makes it very easy for it to release this electron and form a positive ion. In fact, caesium is so reactive that it can ignite spontaneously in air at room temperature.
In conclusion, the ability of an atom to form a metallic bond depends on its position in the periodic table and its electron configuration. While the alkali and alkaline earth metals are the most likely to form metallic bonds, other atoms can also exhibit this type of bonding under certain conditions.
We would love to hear your thoughts on this topic. Please feel free to comment below and share your insights with us.
What is a metallic bond?
+A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond that is characteristic of metals. In this type of bond, the atoms release electrons to form a "sea of electrons" that surrounds the positively charged ions.
Which atoms are most likely to form metallic bonds?
+The alkali metals, such as lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K), are the most likely to form metallic bonds. These atoms have only one electron in their outermost energy level, which makes it very easy for them to release this electron and form a positive ion.
What is the electron configuration of caesium (Cs)?
+The electron configuration of caesium (Cs) is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶ 6s¹.