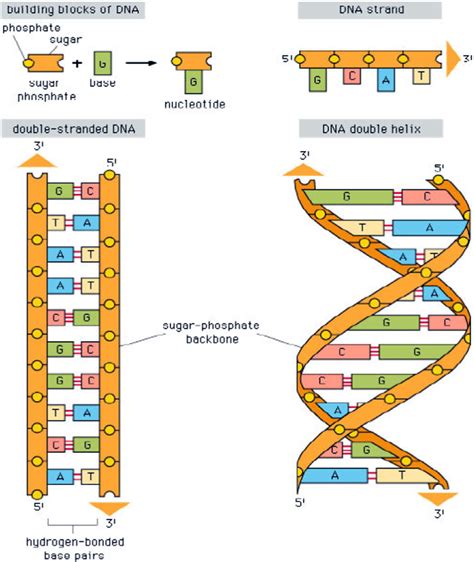
The discovery of the structure of DNA is one of the most significant scientific breakthroughs of the 20th century. James Watson, Francis Crick, and Rosalind Franklin's groundbreaking research revealed that DNA is a double-stranded helix, with sugar and phosphate molecules forming the backbone and nitrogenous bases projecting inward from the backbone. However, have you ever wondered about the specific molecules that form the sides of the DNA ladder? In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of DNA structure and explore the two molecules that form the sides of the DNA ladder.
The Double Helix Structure of DNA

The double helix structure of DNA consists of two complementary strands of nucleotides that are twisted together. Each nucleotide is composed of a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). The sugar and phosphate molecules make up the backbone of the DNA, while the nitrogenous bases project inward from the backbone and pair with each other in a complementary manner.
The Two Molecules Forming the Sides of the DNA Ladder

The two molecules that form the sides of the DNA ladder are deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups. Deoxyribose is a five-carbon sugar molecule that makes up the backbone of DNA. It is called "deoxy" because it lacks an oxygen atom compared to ribose, a similar sugar molecule found in RNA. The phosphate groups are attached to the 5' and 3' ends of the deoxyribose sugar molecule, forming a phosphodiester bond.
Deoxyribose Sugar Molecule
Deoxyribose is a crucial component of DNA, providing the structural framework for the molecule. It is a cyclic molecule, meaning that it forms a ring structure. The deoxyribose sugar molecule has five carbon atoms, which are numbered from 1 to 5. The carbon atoms are connected to each other through covalent bonds, forming a ring structure.
Phosphate Groups
Phosphate groups are attached to the 5' and 3' ends of the deoxyribose sugar molecule, forming a phosphodiester bond. The phosphate groups are negatively charged, which helps to stabilize the DNA molecule. The phosphodiester bond is a strong covalent bond that holds the DNA molecule together.
The Importance of Deoxyribose and Phosphate Groups in DNA Structure

Deoxyribose and phosphate groups play a crucial role in the structure and function of DNA. The deoxyribose sugar molecule provides the structural framework for the DNA molecule, while the phosphate groups help to stabilize the molecule. The phosphodiester bond between the phosphate groups and the deoxyribose sugar molecule holds the DNA molecule together.
Stability and Flexibility of DNA
The combination of deoxyribose and phosphate groups in DNA provides stability and flexibility to the molecule. The phosphodiester bond between the phosphate groups and the deoxyribose sugar molecule helps to stabilize the DNA molecule, while the deoxyribose sugar molecule provides flexibility to the molecule.
Replication and Transcription
Deoxyribose and phosphate groups play a crucial role in the replication and transcription of DNA. During replication, the phosphodiester bond between the phosphate groups and the deoxyribose sugar molecule is broken, allowing the DNA molecule to be unwound and replicated. During transcription, the deoxyribose sugar molecule and phosphate groups provide a template for the synthesis of RNA.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the two molecules that form the sides of the DNA ladder are deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups. These molecules play a crucial role in the structure and function of DNA, providing stability and flexibility to the molecule. Further research is needed to fully understand the role of deoxyribose and phosphate groups in DNA structure and function.
What is the structure of DNA?
+DNA is a double-stranded helix, with sugar and phosphate molecules forming the backbone and nitrogenous bases projecting inward from the backbone.
What are the two molecules that form the sides of the DNA ladder?
+The two molecules that form the sides of the DNA ladder are deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups.
What is the role of deoxyribose and phosphate groups in DNA structure and function?
+Deoxyribose and phosphate groups play a crucial role in the structure and function of DNA, providing stability and flexibility to the molecule.