The human brain is a complex and intricate organ, comprising billions of neurons that work together to facilitate various cognitive functions. Despite its complexity, the brain's structure and function have been extensively studied, revealing new insights into its inner workings. Recent research has shed light on the top spots for local potentials in neurons, providing a deeper understanding of how these electrical impulses shape our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
The discovery of local potentials in neurons has revolutionized the field of neuroscience, offering a new perspective on how neural communication occurs. Local potentials refer to the electrical changes that take place within a neuron, influencing its ability to transmit signals to other neurons. By identifying the top spots for local potentials, researchers can gain a better understanding of how neural circuits are formed and how they contribute to various neurological and psychiatric disorders.

Understanding Local Potentials in Neurons
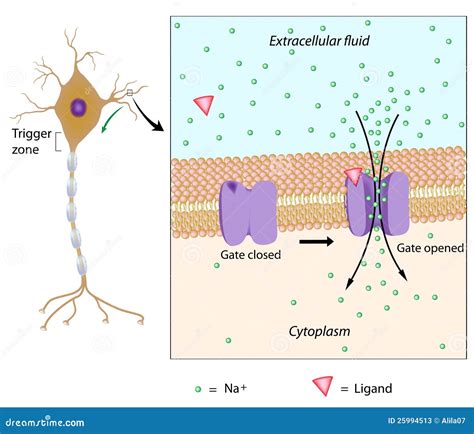
Local potentials are generated by the movement of ions across the neuronal membrane, resulting in a change in the electrical potential of the neuron. These changes can be either excitatory or inhibitory, influencing the likelihood of the neuron firing an action potential. Action potentials are the primary means of neural communication, allowing neurons to transmit information to other neurons and facilitating various cognitive functions.
There are several types of local potentials, including:
- Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs): These occur when the binding of neurotransmitters to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron increases the likelihood of the neuron firing an action potential.
- Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs): These occur when the binding of neurotransmitters to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron decreases the likelihood of the neuron firing an action potential.
- Synaptic potentials: These occur when the binding of neurotransmitters to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron generates a change in the electrical potential of the neuron.
The Role of Local Potentials in Neural Communication
Local potentials play a crucial role in neural communication, influencing the flow of information between neurons. By regulating the electrical potential of neurons, local potentials can modulate the strength and duration of neural signals, shaping our perceptions, thoughts, and behaviors.
Research has shown that local potentials are involved in various cognitive functions, including:
- Learning and memory: Local potentials are thought to play a key role in the consolidation of memories, particularly during the early stages of learning.
- Sensory processing: Local potentials are involved in the processing of sensory information, allowing us to perceive and interpret the world around us.
- Motor control: Local potentials are thought to play a role in the regulation of motor movements, allowing us to coordinate and execute complex actions.

Top Spots for Local Potentials in Neurons
Recent research has identified several key regions within the neuron where local potentials are most prominent. These regions include:
- Dendrites: The dendrites are the branching extensions of the neuron that receive synaptic inputs from other neurons. Local potentials in the dendrites can modulate the strength and duration of neural signals.
- Soma: The soma is the cell body of the neuron, responsible for integrating synaptic inputs and generating action potentials. Local potentials in the soma can influence the likelihood of the neuron firing an action potential.
- Axon terminals: The axon terminals are the sites where the neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synapse. Local potentials in the axon terminals can regulate the release of neurotransmitters and modulate neural communication.

The Significance of Local Potentials in Neurons
The discovery of local potentials in neurons has significant implications for our understanding of neural communication and behavior. By elucidating the mechanisms underlying local potentials, researchers can gain insights into various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including:
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Local potentials may play a role in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- Psychiatric disorders: Local potentials may be involved in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
- Neuroplasticity: Local potentials may contribute to the reorganization of neural circuits in response to experience and learning.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the discovery of local potentials in neurons has revolutionized our understanding of neural communication and behavior. By identifying the top spots for local potentials, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of how neural circuits are formed and how they contribute to various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Further research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms underlying local potentials and their significance in neural communication.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the significance of local potentials in neurons. How do you think this discovery will impact our understanding of neural communication and behavior? Share your comments below!
What are local potentials in neurons?
+Local potentials are electrical changes that occur within a neuron, influencing its ability to transmit signals to other neurons.
What is the role of local potentials in neural communication?
+Local potentials play a crucial role in neural communication, influencing the flow of information between neurons and shaping our perceptions, thoughts, and behaviors.
What are the top spots for local potentials in neurons?
+The top spots for local potentials in neurons include the dendrites, soma, and axon terminals.