Glaciers are fascinating natural wonders that have captivated humans for centuries. These slow-moving rivers of ice and snow play a crucial role in shaping our planet's landscape and influencing the Earth's climate. In this comprehensive study guide, we will delve into the world of glaciers, exploring their formation, locations, and significance.

What are Glaciers?
A glacier is a large, perennial river of ice and snow that forms on land by the accumulation and compaction of snow over time. Glaciers can be found in polar regions, mountain ranges, and even at mid-latitudes. They are formed when the snowfall in a particular area exceeds the melting and sublimation (the transition of a substance from a solid to a gas) of snow and ice.
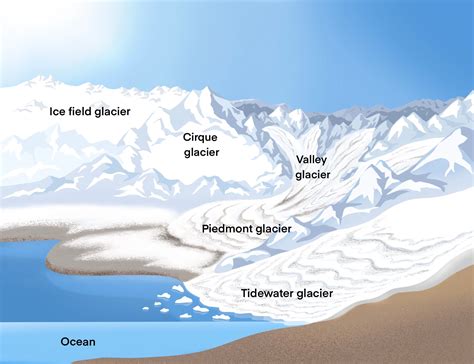
Glaciers are classified into several types, including:
- Continental glaciers: These are large, continuous ice sheets that cover vast areas of land.
- Mountain glaciers: These are smaller, more localized glaciers that form in mountain valleys.
- Piedmont glaciers: These are glaciers that form at the foot of a mountain range.
- Cirque glaciers: These are small, circular glaciers that form in mountain basins.
How are Glaciers Formed?
The formation of a glacier involves several stages:
- Snow accumulation: Snow falls in a particular area, and if the snowfall exceeds the melting and sublimation of snow and ice, the snow will accumulate.
- Compaction: The accumulated snow is compressed by its own weight, causing it to become more dense.
- Recrystallization: The compacted snow is transformed into ice crystals, which then bond together to form a solid ice mass.
- Ice flow: The glacier begins to flow under its own weight, driven by gravity.
Glacier Locations Around the World
Glaciers can be found on every continent, with the majority located in polar regions. Some of the most notable glacier locations include:
- Antarctica: Home to the largest single mass of ice on Earth, covering an area of approximately 14 million km².
- Greenland: The second-largest ice body in the world, covering an area of approximately 1.7 million km².
- Alaska: Home to numerous glaciers, including the Bering Glacier, the largest glacier in North America.
- Canada: Home to a vast number of glaciers, including the Columbia Icefield in the Canadian Rockies.
- Switzerland: Famous for its picturesque glaciers, including the Jungfraufirn and the Aletsch Glacier.
- New Zealand: Home to numerous glaciers, including the Franz Josef Glacier and the Fox Glacier.

Importance of Glaciers
Glaciers play a crucial role in shaping our planet's landscape and influencing the Earth's climate. Some of the key importance of glaciers includes:
- Sea-level regulation: Glaciers help regulate sea levels by storing water in the form of ice.
- Water supply: Glaciers act as natural reservoirs, providing freshwater for millions of people around the world.
- Ecosystem support: Glaciers support unique and diverse ecosystems, including plants and animals that are adapted to these harsh environments.
- Climate regulation: Glaciers help regulate the Earth's climate by reflecting sunlight and influencing ocean currents.
Glacier Retreat and Climate Change
Glaciers are sensitive indicators of climate change, and their retreat is a clear sign of the impact of human activities on the environment. Some of the key factors contributing to glacier retreat include:
- Temperature increase: Rising temperatures are causing glaciers to melt at an alarming rate.
- Changes in precipitation: Changes in precipitation patterns are affecting the accumulation of snow and ice on glaciers.
- Human activities: Human activities, such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, are releasing greenhouse gases and contributing to climate change.

Consequences of Glacier Retreat
The consequences of glacier retreat are far-reaching and have significant implications for the environment, human health, and the economy. Some of the key consequences include:
- Sea-level rise: Glacier retreat is contributing to sea-level rise, which is threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Water scarcity: Glacier retreat is affecting the water supply, leading to water scarcity and impacting agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
- Loss of biodiversity: Glacier retreat is threatening the unique and diverse ecosystems that are supported by glaciers.
Conclusion
Glaciers are fascinating natural wonders that play a crucial role in shaping our planet's landscape and influencing the Earth's climate. However, glacier retreat is a clear sign of the impact of human activities on the environment, and it is essential that we take action to reduce our carbon footprint and mitigate the effects of climate change.
We hope this study guide has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of glaciers, their formation, locations, and significance. We encourage you to share your thoughts and opinions on glacier retreat and climate change in the comments section below.
What is the difference between a glacier and a iceberg?
+A glacier is a large, perennial river of ice and snow that forms on land, while an iceberg is a floating piece of ice that has broken off from a glacier or ice shelf.
Why are glaciers important?
+Glaciers play a crucial role in shaping our planet's landscape and influencing the Earth's climate. They also support unique and diverse ecosystems, and act as natural reservoirs, providing freshwater for millions of people around the world.
What is the impact of glacier retreat on the environment?
+Glacier retreat is contributing to sea-level rise, water scarcity, and the loss of biodiversity. It is also affecting the water supply, leading to impacts on agriculture, industry, and human consumption.