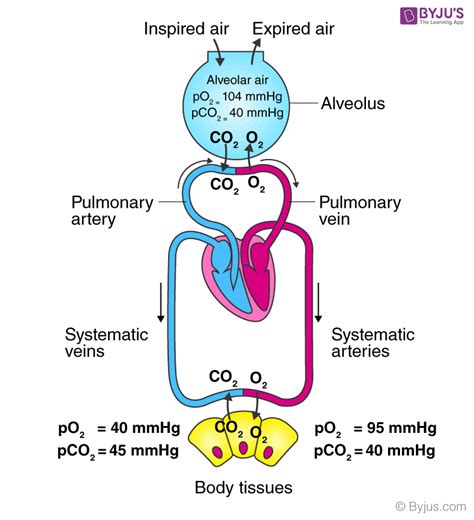
Respiration is a vital process that occurs in the cells of all living organisms, providing energy for various bodily functions. It involves the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency of the cell. One of the crucial steps in the respiration process is the formation of oxyhemoglobin, a compound that plays a central role in oxygen transport and energy production.

The respiration process is divided into three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Oxyhemoglobin formation occurs during the oxidative phosphorylation stage, which takes place in the mitochondria. In this stage, electrons are passed through a series of electron transport chains, ultimately resulting in the formation of ATP.
What is Oxyhemoglobin?
Oxyhemoglobin is a compound formed when oxygen binds to the hemoglobin protein in red blood cells. Hemoglobin is a protein molecule that contains four polypeptide chains, each with a heme group. The heme group is responsible for binding oxygen, and when oxygen is present, it forms a complex with the heme group, resulting in the formation of oxyhemoglobin.

Oxyhemoglobin is a bright red compound that is responsible for the red color of oxygenated blood. It is formed when oxygen binds to the hemoglobin protein in the lungs, where oxygen levels are high. The oxyhemoglobin is then transported to the body's tissues, where it releases oxygen, allowing it to bind to other molecules and participate in various cellular processes.
Importance of Oxyhemoglobin Formation
Oxyhemoglobin formation is essential for the proper functioning of the body's cells. Oxygen is necessary for the production of ATP, which is the primary energy currency of the cell. When oxygen binds to hemoglobin, it forms oxyhemoglobin, which is then transported to the body's tissues. The oxygen is released from the oxyhemoglobin, allowing it to bind to other molecules and participate in various cellular processes, including energy production.

In addition to its role in energy production, oxyhemoglobin formation is also important for the proper functioning of the body's muscles. Oxygen is necessary for muscle contraction and relaxation, and when oxyhemoglobin is formed, it allows oxygen to be transported to the muscles, where it can participate in these processes.
Steps Involved in Oxyhemoglobin Formation
The formation of oxyhemoglobin involves several steps, including:
- Oxygen binding: Oxygen binds to the hemoglobin protein in the lungs, where oxygen levels are high.
- Heme group binding: The oxygen binds to the heme group of the hemoglobin protein, forming a complex.
- Conformational change: The binding of oxygen to the heme group causes a conformational change in the hemoglobin protein, resulting in the formation of oxyhemoglobin.
- Transport: The oxyhemoglobin is then transported to the body's tissues, where it releases oxygen, allowing it to bind to other molecules and participate in various cellular processes.

Factors Affecting Oxyhemoglobin Formation
Several factors can affect oxyhemoglobin formation, including:
- pH levels: Changes in pH levels can affect the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin, resulting in changes in oxyhemoglobin formation.
- Temperature: Temperature can also affect oxyhemoglobin formation, with higher temperatures resulting in increased binding of oxygen to hemoglobin.
- Carbon dioxide levels: High levels of carbon dioxide can affect oxyhemoglobin formation, resulting in decreased binding of oxygen to hemoglobin.

Clinical Significance of Oxyhemoglobin Formation
Oxyhemoglobin formation is clinically significant, as changes in oxyhemoglobin levels can indicate various diseases and conditions. For example:
- Anemia: Decreased oxyhemoglobin levels can indicate anemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin.
- Respiratory disease: Changes in oxyhemoglobin levels can also indicate respiratory disease, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Cardiovascular disease: Decreased oxyhemoglobin levels can also indicate cardiovascular disease, such as heart failure.

In conclusion, oxyhemoglobin formation is a crucial process that occurs in the respiration process, allowing oxygen to be transported to the body's tissues. Understanding the steps involved in oxyhemoglobin formation and the factors that affect it can provide valuable insights into the proper functioning of the body's cells.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of oxyhemoglobin formation in the respiration process. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to ask.
What is oxyhemoglobin?
+Oxyhemoglobin is a compound formed when oxygen binds to the hemoglobin protein in red blood cells.
What is the importance of oxyhemoglobin formation?
+Oxyhemoglobin formation is essential for the proper functioning of the body's cells, allowing oxygen to be transported to the body's tissues.
What are the steps involved in oxyhemoglobin formation?
+The steps involved in oxyhemoglobin formation include oxygen binding, heme group binding, conformational change, and transport.